As found on YouTubeHuman Synthesys Studio It’s Never Been Easier To Create Human Spokesperson Videos. No Learning Curve, So Easy To UseMatrutunb Diamond Painting Kits, Diamond Art Kit,5D Diamond Painting Kits for Adults Full Drill Round for Wall Decor, Gifts, Relaxing https://t.co/RTAsPUmKoM https://t.co/cDWKPRGtZS
— Ralph Leaman (@LeRoyMoco) July 25, 2023
Author: Leaman Ralph
Really sugar is shaky because it originates from a straight stick see the play is Granny yes Grandma plus new style luv MaryJane so listen (Granny Apple last years blue ribbon production winner AKA) I, I, I ain't on the right side of my house Jane something or the other is in my room: finally after an extermination Grannie speaks once more "let my (old man) Pacman step on it". See it is home on the range so solo as it be truity speaks got a problem it is your own. But alter scenario: Z/n time; narcotics I got that candy s.p.ee..d360 Bar itch its' and Mickey Mouse for the Sultan 7 1 4er well a hem a hem, it went early in the morning like a smack chanting sugar structure 7 -one 1 +eleven and 4 do an ate 'er 8 eight 'er? Well that aint nice. NARCO says do you know them numbers change (response) Yes it is a FiX they are MF's Ope yeah Ope Douglas is it.
Surrounded by Alkaloid is both Mary and Grandma in an never ending circle of membership. French mandates declare put up their dukes... ZEN Pepsi can talk half Chocolate and your ole man Pacman down in Cuba posing as the worlds one and only Coffee Wizard "back 1:1" tis Coffee time... ||
hey guys so um I guess I’m just making this video is kind of like an update video kind of thing this is honestly in a lot of ways like a really sad video um I’m sorry to say it but um it just kind of feels weird right now I guess like with this just happening this week I guess just kind of going making normal videos and just kind of ignoring it I guess so I guess that’s kind of why I’m making this video today yeah I’m not going to lie to you guys honestly like it’s been like a really awful just really sad week in a lot of ways of course on the camera you know I always want to try to be positive for you guys and stuff and still trying to do that but yeah um a lot of you guys probably know um because I’ve already kind of imposed to kind of my other socials and stuff that my grandma unfortunately passed away um this week um it was like almost a week ago today when I’m making this so it’s kind of crazy I feel like time has just been like really weird right now and this has been not really the best time in a lot of ways this week right now this week like things have just been really awful and things have just been so sad obviously like I’m so sad to lose her and just really miss her a lot already and I don’t know I guess it’s just been a really crazy time because she’s been with us now guys for like so many years even growing up like when I was a kid she was around a lot she was like always at her house and I guess like this happening like um like things have honestly been getting pretty bad because I think that my grandma had like Alzheimer’s or dementia you know something like that where like it causes like a lot of like memory issues and things like that especially lately like things have just been getting like pretty bad it’s still just kind of like I don’t know it’s still so sad to just kind of like finally see that happen and throughout all of this we just kind of been trying to do like everything that we can help her and be there for her and have nurses over bring her to like appointments or anything like that like whenever she needed it so um you know not that this is about us this is like about her even growing up like I spent like so much time around her and she’d like always be over and um you know we just were together a lot in a way I guess that kind of makes it even harder just because like you know you grew up having this person around so much and now they’re not anymore a lot of like good memories with her when I was younger like my grandma always loved the beach so like every summer we’d go to Rhode Island and she would always come with us which was really nice and then when I was in school she would like be around her house a lot so my school would like do this thing called like Grandparents Day like she would like come by in school and like kind of just like spend the day and it was always really nice having her there and I always really appreciated her coming I still remember like there was a trip we took her to in Chicago go and crazy now guys but um when I was like really young I was like a really big Jonas brother fan and my grandma came to see a concert there she got to meet their bodyguard Big Rob I think she met the Jonas Brothers too I’m like it’s so long ago now that like I kind of don’t remember I remember she actually really liked them she was like oh they were so good and yeah she um she loved them and she liked that trip and everything and you know it’s just really fun like traveling with her and you know I’ll always be really grateful for like all those good times that we had and I don’t know you guys like just kind of like the last few months like seeing like how bad um like I guess thanks for getting with her it’s just been really sad and really scary sometimes we were having nurses coming over almost every day also just kind of trying to like help and you know be there and um you know like doctors like physical therapists she was having like speech people coming over because she was having swallowing issues as well like the last few months and yeah I don’t know it’s definitely just been a really really like crazy time and for me it’s just kind of like I really like hate to see my grandma being in pain at all I guess that’s one thing is like at least now she’s free of that in a way but it’s still just really sad yeah it’s just really sad to like witness that for a while now things have been getting like just really bad I’m never trying to like complain too much or anything like that but this is kind of like a dedicated video about this whole thing so I guess here hopefully it’s okay to talk about it I’m definitely not trying to be like oh feel bad for me guys or anything like that you know I totally get I was really lucky to have so many years with her and I’ll always be really grateful for that too it’s really sad I guess like you know seeing her in so much pain and also now a lot of my family has been taking it really hard and I hate seeing them in pain so I’ve also been trying to be there for them as much as I can sometimes I feel bad because it’s like you know there’s nothing like I can really do to make it better but I still want to like obviously try and stuff and yeah and um because like I won’t fully get into it but you know just like what she was dealing with like it was definitely getting really bad I think in like a way it’s like of course I know like she wasn’t going to live forever she did live a really good long life you know she was 95 years old yeah it’s just I guess still just like seeing it finally happen and also seeing like my family being I’m so upset and everything like that is just really hard for a while also my grandma was just kind of like in and out of the hospital and we were always trying to bring her there whenever she needed to go but the last visit she was there was actually pretty recent and it was really scary because like when they were discharging her I was kind of surprised they were discharging her because she was just seeming still really bad like honestly when I saw her in there it was kind of scary she just seemed like so out of it she wasn’t very responsive and I was kind of like even the day they were releasing her it really wasn’t that much better coming home it’s like there would be moments that were like a little bit better which of course that’s always good to see but also a lot of times that I guess kind of were just like not like where she’s still just kind of like stay unresponsive and the hospital already released her so it’s just kind of like we just kind of have nurses home helping and it’s just kind of hard to know like what to think and now I guess this is where we’re at so yeah but like last hospital visit was like pretty worrying and I’m definitely not trying to make this like a feel sorry for me video or anything like that like you know I just kind of want to update you guys on the situation I know a lot of you guys really love seeing her in my videos too it’s like I almost didn’t even know if I should like make this video or not make it like if there’s any point or not but it’s just like the reason I guess I kind of decided to is because like I kind of said earlier it just kind of feels weird I guess just kind of going and making a normal video right now and not addressing it at all on here so I guess that’s why I’m making this so hopefully that’s okay but um I will definitely say you know I always will be really grateful for the times that I did have with her and for having her around as long as I did and that she lived to be like 95 which even though it’s like really sad that she is gone now you know I guess I can just kind of hope that she’s at peace and pray for that and um you know just be grateful for the times that like we did have together and I always will be really grateful for those times I also just really did want to like get on camera and say thank you so much to every single person that has sent me such nice messages honestly this has been like a really hard week so every single person that message that has messaged me I really want you guys to know that like I just appreciate that so much and um it really means so much right now guys like that’s one thing that at least makes me feel a little bit better so thank you guys so much for that also I’m sorry that I know I have not been the most active this week um which hopefully you guys understand one thing that I kind of do want to address and like make clear is like the day before this happened I was actually having a really fun night and a really fun day like on Tick Tock I was on there a long time that day because I’ve been doing a lot of tick tock live which I’m doing a lot more of now which I definitely want to keep doing because I’ve been having a lot of fun on their um I was actually having a great couple weeks and then and then this day happened but you know I guess sometimes things in life can just change really fast but yeah there was like people thinking that that night or like that day was the day I was just on Tick Tock having fun um and I just want to be clear to you guys that absolutely not I was not like whoa I’m so happy like whatever that day at all um that was actually the day before that was I think Sunday and then this happened Monday so literally things went from being like really happy to the next day literally my grandma passed it was just a lot of crying around the house it was a lot you know so I just want to be clear that was not the same day I was like not partying on Tick Tock that happened the next day I think even though like you know we were seeing a lot of things going like you still never really expect it at least that’s kind of how it was for me and that was the next day that was not the same day I’ve been seeing some comments saying that and like making some really just not so nice jokes and jokes about me at the funeral and it’s like and it’s just kind of like I don’t know it’s like I don’t I’m not going to focus on that too much because I really appreciate the people that have been being so so nice but yeah the people that are thinking that or that I’m doing anything like disrespectful to her at the funeral or anything like that it’s like no that’s definitely not the case that would never be the case I would hope most you guys know that and yeah literally that happened on the next day that she passed so that was to totally separate days this is like the grandma from my mom’s side and it’s crazy because she has a lot of people past um on pretty much almost everyone that’s like on her dad’s side and now my grandma and that’s both her fire and said I think she’s just kind of been taking it like really hard so I feel so bad seeing that and I’ve really been trying to be there for her as much as I can out of respect for my family some of them don’t like being online so I always want to respect that and I never want to you know kind of like call them out by name or like you know put them out there if they don’t want to be out there but also some of them like have been taking it really bad and I feel so bad seeing that you know and of course like you know I want to try to be there for them if I can sometimes I feel really bad because I’m not always like even sure what to do and you know I always try to like just like tell them even if there’s anything I can do of course I want to but it’s just kind of so hard to know like what to do in this situation and sometimes even they’ll tell me or you know I kind of know like there’s really nothing I can do to like make it better and I feel so bad because like I really wish I could it’s also sad on top of her being gone just seeing them being so sad and just like I guess being around just like so much sadness right now um but you know I guess it just kind of is what it is guys and I guess like Things Are Really Bad Right Now I just kind of have to try to stay positive and remember the good things and at the same time like I know she’s in like a better place than at peace and everything at least there’s that and in a way I kind of do want to get back online because like you know sometimes my family they just want to be alone and I get that too it’s like I don’t want to be always in the way you know but in a way it’s like that one I’m just kind of by myself and just kind of like in my room it’s like I don’t really feel like that does me any good either or makes anything better because then I’m just kind of being sad doing nothing in my room so I think I am going to try to be online again sorry to you guys if I’m not the most consistent right now or like whatever because it still just kind of is like a really sad like situation but you know I guess I can just try to stay positive and stuff yeah you know try to get back online for you guys and everything and then I just kind of feel like sometimes just sitting around here just kind of doing nothing is just kind of making me more sad um but yeah you guys you know my grandma was a really amazing Grandma um I’ll always love and miss her I am happy it’s like on a four positive thing on a more positive side guys because like ah I’m really sorry to make this video like so depressing I feel like this has been like such a sad like video so I hate to be like that but I am happy that I did get to like share some videos and times with her with you guys on here and I’ll always be grateful for the good times that I did have like I said and you know for the good things in life in general I think that’s always important to focus on even when things are really hard and bad so I don’t want to make this just like all really sad or anything like that and you guys don’t have to feel bad for me by the way I feel like some people are going to like see this video and be like she just wants sympathy or like whatever and it’s like no you know I completely understand I was very lucky to have as much time with her as I did I think even during these really hard times and I think these kind of times are hard for everyone you know it’s also hard like I said I feel especially bad for like my family and everything like that it’s like I think it always is good at the same time to try to focus on the positive things and try to stay as positive as you can so of course I still want to keep going on and keep trying to do that and stuff I did kind of want to share this with you guys though because I know from like the videos that I’ve posted and stuff like that that a lot of you guys also really loved my grandma like those were some of the really positive comments I would get a lot of you guys would be really positive towards her and I think just really also loved my grandma so I just kind of wanted to fill you guys in on that thank you guys so much for all the nice messages and I guess that’s really all I can say about it but next video will probably be more positive guys and I hope all you guys are doing good thank you guys all again so much I love you guys so much and I really appreciate everyone that’s been really kind during this time I guess I will see you guys in my next video so all right thank you guys bye
Christ Is the Firstfruits, and We Are the Harvest – The Tabernacle through the Eyes of Christ #18
Don't say you are a Christian. Don't parse words with me. Don't play games with me. You are a Christian when you are following Christ, period. You're not a Christian because you come to church one day out of the year. You're following Christ. And following Christ doesn't necessarily mean you come to church either. How's that for putting it the way it is? But you're following Christ, which means you are studying Him. And “Him” is not a pronoun limited to one book or one half of a book. It's the whole thing. ♪ ♪ So, we've been in a study now, I think 17-plus weeks, looking at through the lens by way of the New Testament, looking into the Old Testament.
We started with looking at the tabernacle, its furnishings, we moved on to the offerings, and now we are kind of in the set times. And it all ties together, but I've been trying to say this over and over and over again. And maybe you'll hear me repeat it a few times, even in this message today. You've got repeatedly things that are; they are types of our Lord. They are pictures. They are things that when we read them, let's just put ourselves in the Old Testament saints' shoes for a minute and there is no New Testament, just for a second, we would only be seeing one dimension, what God said to Moses, “These are the directions.” That's all we would see, all we would know; we wouldn't know that there's more.
So not just the practical application, but we, reading the full book can see the prophetical application and fulfillment in many of these things, pointing to Christ. Now if I sound repetitive on this, it's because this is what this book does. A lot of people say, “Well, I don't, I don't bother with the Old Testament because it's the Old Testament.” That is the dumbest thing I've ever heard. I'm sorry, but that is. Without this Old Testament, even reading the New Testament doesn't really make sense. You know, if you're reading “Jesus, born of a virgin,” ah, okay, but if, if you're reading the Old Testament and you can see that there were prophecies foretold that our Lord would be born of a virgin, that certain things foretelling, that's why you need the Old Testament. You can't do away with it, and why would you? It's only those people who really don't understand why it's here or they are adherence to the old way.
They are still slaying saber-toothed tigers, even though the saber-toothed tiger doesn't exist anymore. So we, we've been looking at, we started with the Sabbath, Passover, the Feast of Unleavened Bread, marking the beginning of Israel's feasts, commemorating the deliverance of Egypt, out of Egypt's bondage and the first harvest of the year. Now the New Year would later be marked out in the fall season, so we have two New Years to deal with eventually, but I'll explain that in a minute. All of these set times, all of them, first and foremost in their practical setting, were to remind the children of Israel that time, as well as attorney; eternity, as well as everything else, belonged to God. Now, see, sometimes I think these people were really fortunate because, well, they were. They had the direct sight of everything that happened.
We are living generations after and we are having to, by faith, take everything that's here. They got to see firsthand. So if you think about it, if you lived in that day, you might be a little bit better off in some respects, unless you were the stiff-necked, rebellious children of Israel, but you might be better off in that there was some type of connection. I mean, imagine if you were in Egypt's bondage and you saw the plagues poured out and you saw the most powerful ruler in the then-known land basically succumb to the words of God, letting the people go.
I mean, something tells me it'd be a little bit different than how we are in today's day and age, very distracted, it's take it or leave it. We're all in this very, “I'm not sure it really happened, did it happen that way?” And so to really assess why God made these set times, which I've said already, the set times have a connection or a correlation to Israel's history or in general the history, for example, the Sabbath takes you right back to creation. But much of these set times as we begin to study them, we see that God is saying, I want you to remember something in perpetuity, your deliverance out of Egypt's bondage. And why is that important? Because you could read this, just reading the Old Testament here and say, “Okay, I got it already; they, God delivered them out of Egypt's bondage.” But what if Egypt's bondage is God delivering you out of a life basically with no God, full of sin? If that's, then it would be remembered. It would be something you'd keep thinking of and you'd be grateful for that God opened your eyes, that He found you.
That's called prevenient grace. So when God says to remember their deliverance over and over again, yes, He's talking about that specific act, but we who are reading this should remember two things. It's a double; it's a double whammy for us. The first one is that God made good on His word to deliver the people. He said they would go in to a land that was not theirs, they'd be strangers in that land. They'd come out of that land, greater in number, richer, etc., which they did. And then you've got the double whammy for us as Christians, understanding God has called many out of the darkness into His light and that is the same as being delivered from Egypt's bondage. Your, your eyes have been opened.
So don't think, don't just read it in a one-dimensional way. Now on the fifteenth of Nisan, which is the equivalent to our April, depending on when it falls, but usually it's equivalent to April, the Feast of Unleavened Bread began. It went for seven days; no leaven could be consumed. And we read often a term, if you've ever seen━how many of you have ever seen a Passover booklet called a Haggadah? Okay, so it's a little booklet and basically it's, we'll call it the synopsis of the deliverance story, okay? But what's interesting is the Haggadah, the name on there, “festival” or “festivity,” we don't tend to think about this, but the Passover was referred to that. And in fact, there's a passage in━let's see if the brain's working good here━in Exodus, I'll read it to you if I can find it. Okay, here. So Moses is talking to Pharaoh and he says━“And afterwards Moses and Aaron went in, told Pharaoh, Thus saith the LORD God of Israel, Let my people go, that they may hold a feast unto me in the wilderness.” Now why is that interesting? Because that word is we'ahogu, which is very much, because it's a Semitic language, it's very much like the Arab word hajj.
They're just pronounced differently. So we have that same concept, a “pilgrimage,” or “wandering,” if you will. And these feasts or set times, don't think that they just happened like God said, “Okay, we're going to have a party now.” They were all to tie back, as I said, either in creation, Israel's history, things that God wanted the children of Israel, and after that, us, we who are of the new dispensation, to think on, believe, and obviously this is where I'm going with this.
So we're tying the old feasts and showing how they connect into the New. The law instructed the children of Israel that when they entered the land; this is always missed; when they entered the land, the Promised Land, the land that God said they would enter into and reap the harvest, that they would bring a sheaf of the first grain to the priest who would weave it before the Lord on their behalf. And there's something that I don't know why it's missed often, but I have it open in front of me and I'll read it to you as well from Leviticus 23 and verse 10, “Speak unto the children of Israel, and say unto them,” listen carefully, “When ye be come into the land which I give unto you, and shall reap the harvest thereof, there ye shall bring a sheaf of the firstfruits of your harvest unto the priest.” So clearly, a lot of times people think━first, how could you do a harvest and practice a real true harvest if they wandered for 40 years in the desert? Hello.
So I mean, you could probably harvest some things, but you're constantly moving. So He clearly says, “When you come into the land which I give unto you,” and that's key to understand how this would become regulated and obviously everything in the law becomes regulated. So by yielding and offering their firstfruits of their harvest to God, the first of it, they acknowledge that they were dependent on God for the harvest yet to come. And this is the other thing I'm finding people━you only know what people mess up when you start to read what people have, in good intention, I'm sure, penned. There's a lot of confusion about Firstfruits that is the gathering of the first of whatever and the feast of ingathering, which happens as we'll call it the full-orbed, full-blown harvest at the end of the season, okay. There's, there are differences here. So this particular Firstfruits would have been observed with somber tone.
The sheaf was to be waved on the day after the Sabbath. What we New Testament folks, I refer to this in my message on the Sabbath as the Lord's Day because it's the day the Savior rose. And the apostle Paul refers to Christ, in 1 Corinthians 15:20, as “the firstfruits of them that slept”" So this act, if you will, of our Lord's, of basically of dying and resurrecting and ascending, but the death and Resurrection portion, the Firstfruits hallowed the harvest from which it was taken. So I want you to think on why Firstfruits is important. Now, don't get me wrong, the late Dr. Gene Scott taught on Firstfruits and made it an integral part, if you will, of giving in this church, which people would basically first of the year and whether it's your first paycheck or the first of anything usually, and that's how it was taught.
I'm not saying that that ought not to be done, but there's something actually, in my opinion, infinitely more important than that, and I'm going to tell you what it is. If let's just say we go to glean the firstfruits of whatever is coming up and we're choosing the choicest and the best, it is a type. We're saying; we're not saying, “Oh, I hope that the rest of the harvest is going to be like this.” The firstfruits that we would be offering to God in the agrarian society would definitely be the expectancy of the rest of the harvest.
Does that make sense? Good, because now I want you to think about what Paul wrote when he said, “Christ is the firstfruits of them that slept.” For the Christian, we should expect, it shouldn't be; I don't know why I've done how many funerals and I still see people doing this very same thing, not understanding their faith. And that to me is the greatest, if you want to know what a crime is, that's a great crime because Christ died, went first as the first Goer. We have a right; we'll call it the right of expectancy that we too will be like Him. We too shall rise. That's the concept that for me, the most important concept of Firstfruit to recognize that something like this had not happened before. And don't get Lazarus confused in the mix. Lazarus was called forward to show Christ had the power over the grave and over death, but Lazarus still had to die.
So he's called out of the dead. Deliberately we know that the passage tells us that he was in the grave, and it's either Mary or Martha says, “You know, by now he's going to be stinking. It's been, so”━you know, it's well beyond the third, fourth day now. And that was deliberately put in there because you could not be considered certifiably dead unless three days had passed.
So we know Lazarus was certifiably dead when Christ called him out of the tomb, but that is not the Resurrection. He did resurrect from the dead, but he'd still have to die again, a normal death, and then like everyone else, hate to say it like this, but Lazarus is not like, he's not an exception, like everybody else, all must die. And this is why that expression that says, “Unless a grain of corn go into the earth.” It takes something essentially that looks dead to bring life. So here we have Christ as the first Goer and what was removed, and you're looking at these feast times, what was removed, the impediment, was the ceremonial impurity, and I'll explain what I mean by that.
The relation that the Firstfruits sustain the harvest is one thing, but remember the steps that had to be taken before. So if we understand the laws of the offerings that we looked at, and we kind of string this together, I hate to say it, like beads, it becomes clear that these times were set up with special times before or after one could be cleansed. Let's just say if you were making a sin and trespass offering, and then this would be offered or this would be celebrated. So God had a way of basically making sure everyone could be included if you went by the prescribed method, which we're looking into right now.
And if you're curious to know, Leviticus 23 spells it out. You've got a couple of passages in Exodus, Exodus 23, I believe━don't quote me on that, but I believe it's Exodus 23 as well. And then in Deuteronomy and Numbers, you've got some kind of extra material there, so yours to kind of pick apart. But when I, and you're going to hear me repeat this throughout this message. If the same relationship that the children of Israel had to the harvest, that is the Firstfruits, the expectancy, the, “Okay, we offered, we took the Firstfruits and we offered the best to God”" we are following the same pattern as Christ is the Firstfruits.
We should be expectant. Not “I expect and it may not happen.” No, that's the first harvest of the Resurrection; we are all going to follow that harvest. There's only one criteria, that you remain connected in faith and trust in Christ. We will all be in that harvest. So it's important to understand, or if you want to say, “If He's the Firstfruits, we will be the harvest,” that is the expectancy of the hope that's promised to the believer. Now the apostle Paul also wrote, “He was delivered for our offenses, raised for our justification.” So God laid upon Him, you've heard me say this before, all the iniquity of us all, and it would not have been a finished work had He not, had God the Father not laid that all upon the Son. As for Christ, the law had no further claim to urge penalty or to exact. Hence, He could be raised up from the dead to take His life again. Remember, He said, “I take my life, no one takes it from me.” So even though; see, these are the things that I, sometimes I have to stop and just scratch my head.
Jesus said, “I take my life, I lay it down, I can pick it up again,” essentially. So it makes no sense to me when I hear our Jewish brothers and sisters get very offended when we talk about the act of crucifying Christ. And the reality is, if you think about it, Christ had to die one way or another. If, if His plan, what He says, something's wrong with the world and only His death could fix it, He had to die one way or another. And it always comes down to this, people with lack of understanding will get very offended when we say the religious leaders basically urged Pilate, and the religious leaders were the ones kind of angling for this. Back to my message and my notes here; like the wave offering, waved to be accepted for the people by God, I'd say that Christ also became the wave offering, not accepted by God, but accepted for us by God. There's that little addition that makes everything count. The Firstfruits was the earnest of the upcoming harvest, a pledge that the harvest would be gathered, and there's also a special set time for that, that God says, “And this is harvest time.” So, if we want to talk about this particular Firstfruits, we can't, in this particular subject, we cannot not talk about the Resurrection, because that is how we connect to the New Testament over and over again.
And several times you'll, you'll hear me mention, especially about it, the apostle Paul will mention Firstfruits. So, it's important to understand the connection there starts at the Resurrection. And if you remember the only sign when they came to Him, they said, “Give us a sign. He said, “There'll be no sign except the sign of Jonah,” which was to say, “three days and three nights,” or at least being in the giant fish's belly, only to be spewed out alive, which if you think about it, we're not going to take this too far to the extreme. But that was Christ basically saying, “You want to know what My guarantee is? Now, your guarantee is Firstfruits. Mine is the sign of Jonah.” And you can take that however you want, but Jesus to us, Jesus is the new covenant. He's not just representing a covenant; Jesus is the new covenant, much like the old when it was given, a promise that God would make good on His word, so here Christ is telling these people, basically, “The only sign you're going to get is the Resurrection,” which Paul calls Christ “the firstfruits of them that slept”" He's the first of his kind.
So forgive me for making a circle here, but just as we are connected to the first Adam in our fallen condition, because of nature, condition, etc, we are indeed condemned. It's a death sentence, being born in Adam, in the first Adam, but being born again into the second Adam or the last Adam, which is Christ, brings life. It is the, we'll call it the reconciling or the making right, what was in the beginning, we have now access to the Father by this avenue, the one named Jesus Christ. And not only that, not just access, but the promise. This is the whole amazing thing, in my opinion, about studying these set times. See, these people didn't have a promise of eternal life or immortality. They didn't have that promise. They knew that the first parents had given it away.
We have that promise though, which makes wanting to know about this Firstfruits. As I said, you can talk about the giving part of it, the component of giving, which is important. But I'd like to start with the most important, which is what, why we're here: “If Christ has not risen, our faith is vain.” And I'm not interested in having the discussion with people. Let me just say it now, so I get it out of the way and, and you know, you can be angry with me later if you want, or you can be angry with me now. I do at both. Don't say you are a Christian. Don't parse words with me. Don't play games with me. You are a Christian when you are following Christ, period. You're not a Christian because you come to church one day out of the year. You're following Christ. And following Christ doesn't necessarily mean you come to church either.
How's that for putting it the way it is? But you're following Christ, which means you are studying Him. And “Him” is not a pronoun limited to one book or one half of a book. It's the whole thing. That's what makes you a Christian; you're following Christ, you're learning about Him. It's like saying, “Yeah, my family.” Well, if you spend time with them and you live under the same roof or your blood, born blood, or; but there has to be a connection there to say that. You're not going to go to a stranger out there on the street and say, “Ah, that's my, that's my family over there.” That person's going to be looking at you and saying, “Call 8-1-1.” Not 9-1-1, 8-1-1.
Do you know what that is? 8-1-1 is the number you call before you dig a hole, courtesy of the power company. All right, so what makes the difference here? These people didn't have the promise of Resurrection, but we were given that. Christ said, “I need, A) to go away that I might send the Holy Spirit.” Number two, He had to go away showing basically that this was the pattern planned by the Father. His public ministry would give enough time, demonstrate enough miracles, explain enough about why He came. And then the rest was left back, if you think about it, the rest was left back with humankind, “Now you go out there, you teach, you go make disciples, you go make learners of every nation.” He didn't say, “I'll come back and I'll do that work for you.” He said, “Now you go out and do it.” Just as the first Adam was told to go and tend and till the earth, we in the second or last Adam are still tending and tilling the earth, but it's in the human form that we do it, not working and laboring for the ground.
So there's a lot of, I'm sorry, just a lot of confusion. It's very frustrating for me because I find people, even some who have a good intention, would like to tell you that, “You know, if you come on Easter, it's enough.” That's just a show. How would you like to be married to somebody and you only show, you only come home once a year? It's kind of like that, okay? I don't think that's a marriage, by the way; anyway, enough of my opinions here. So we know, by the way, why Paul wrote, “For we know that when he shall appear, we shall be like him,” because we shall be like Him. That is the promise of Firstfruits, and this is why this is so vitally important. The same Spirit of God that opened up the believer's spiritual eyes, that raises us from the death of sin and the life of righteousness in Christ, descends upon a lifeless body.
Now the Spirit's already in the person, but there's also that, what I call the, that the helping Spirit; and don't quote me on this, I'm just trying to make this as clear pictorially as possible, that takes the final, final claim on what is inside the believer. So that means whatever the person's person was, plus the Spirit of God. You remember, I taught on this many years, the part payment, the arabon, it's called in the Greek. Now that ticket is turned in for the whole person, not just, “Hey, I tag you with my Spirit because you belong to Me,” but the whole individual. That means everything in my memory bank, all that I━not this shell, but everything that I am at the point of death basically is released with the Spirit to be with God until a new body, until the time that a new body will be granted to every single believer in Christ. So here's the kind of, we'll call it the litmus test.
I'm curious to know how many people actually believe, don't answer me; I'm curious to know how many people actually believe what I just said because you know, people actually believe that it's very clear to me that we deceive ourselves all day long. You know, you, you, you can be a biohacker, you can be engaged in fitness, eat the cleanest diet, have the best mental health. And when God says it's your time, it's your time. You don't get to bargain. You don't get to plea deal. It is what it is. So this is what is all equally baffling. If you knew and understood, which I hope that every creature that's born on the earth can come to understand and know that there's a terminus to life.
Don't think I'm talking like the grim reaper. This is actually a message rooted in extreme hope and certainty of what's said here that I wouldn't be looking at that day and saying, “My God, no, help me for I'm not ready to go.” No, when that time comes, the expectancy, because I've known; I'm sorry to say this, it's going to sound a little bit funny when I say this, but I've known the Firstfruit for a long time.
And I'm not trying to be blasphemous when I say that. So if I've known Him for a long time and I've built my relationship on that, then when I come to that hour, that moment, I have the expectancy and it's not something that may or may not happen. This either happened, He either died and rose up or He didn't. Now that, I think we've settled in many messages on the Resurrection. So if a person has settled that and you believe that this is absolutely true, that a man, all-man/all-God died, was put to death and rose from the dead, then the expectancy for you and for me should be just like these children of Israel with the Firstfruit of the harvest. They went in there looking for the choicest and the best, presenting it first to the priest as a wave of offering and presented to the Lord with expectancy, that the rest of the harvest, not━and expectancy is a bad word because it leans towards, is there a possibility that it may not be as good as the things that we offer to God, but in fact it's the promise that what we rendered to God at the first, the rest of it, it's putting God first, God takes care of the rest of the rest, but the rest will be just as bountiful and just as good.
And that's why it's important to make these connections between those Old Testament saints and we who believe in Christ, we who faith and trust Christ for our salvation. So I'm going to try and paint a little picture here that gives some understanding because there's a lot, you know, in these feasts there's a lot to think about. Of course there is the sowing of seed, the caring for, ultimately the harvest that would be reaped. And I can tell you as someone who has just recently started growing a lot of food, it's hit and miss. You plant a seed and you can hope and pray, but trust me, the passage says, “Thou shall not kill,” I've probably killed a couple of hundred plants of late, okay? Some people have that green thumb and some people don't.
But imagine this is, you can't just go down to Publix or Vons. You're in the desert, wherever you are, this is your food supply. This is, if it's messed up, you're all going to starve. I want you to think of it in that respect. So going to get those, planting the seeds, taking care to tend and then seeing the first harvest, the first thing that comes out of the ground would be almost, silly, but miraculous. And if the rest of the crop came out like the first part, that'd be even more miraculous, but that's the promise of what God basically was saying, “Put Me first, I'll bless and take care of the rest.” Now the prosperity people get a hold of this and they milk, manipulate, and twist the heck out of that verse to make it mean something that it doesn't.
And you're never going to hear me talk to you about something like that because I don't do that. That's not what God promises either. God's blessings, if you're really interested, you've probably received more and I've probably received more in terms of blessings than most people I know, and they're not tangible. They're not tangible. To be able to stay in the faith. Look, we're living in an age of crisis and chaos and craziness. To be able to stay connected in faith, still look unto Him, still have the sense that I belong to Him no matter what's going on in the world I'm okay because He's got me and I've got Him! Now at the temple time, because remember it said, “When you come into the land,” so I'm going to jump to the temple time. But at the temple time, messengers of the Sanhedrin, those dirty rats, they would go out from Jerusalem on the evening of the feast and they would bind all of the tall standing corn and bundle it to make it easy to be taken up.
See, they had all these little ways of getting around God's rules and regulations and this is one of them by the way, it's kind of interesting. And no wonder why God said, “Enough.” If you keep trying to find ways to sneak around God's back, I think God eventually is saying, “I saw all of it. I didn't just see one time, I saw it all, you children of Israel, you,” all right? Sometimes it's hard to say what you want to say. All right, later at the time of the temple, the grain would be threshed with rods so that the barley corns were not injured. After this it would be parched over an open flame, winnowed in the wind, and that would remove the chaff. Finally the barley corn would be milled and put to an extensive sifting process until it was sifted finely. And to show you how; sorry, how nutty this was, according to the writings in the Talmud, the sifting would go on and on and on and on and on and on until a temple inspector/priest could plunge their hands into the flour, remove the hand without any flour adhering, and then it would be ready.
But I mean the procedure that they did just went on and on and like overkill. But anyway, that, that's their business, not mine. So the sixteenth of Nisan, the Firstfruits were presented to the Lord, an omer of barley, which would equal approximately five pints, was mixed with three quarters of a pint of olive oil and a small amount of frankincense was sprinkled upon it. This was the Firstfruits offering. It was then waved before the Lord by the priests in accordance with Leviticus 23:11-13. Firstfruits was a national observance, not just a singular. So each family at this set time would have to bring their Firstfruits. Every family, one set, one set offering for each family unit, right? So you're not; if you have five people in the family, five people aren't offering Firstfruits.
It's offering from that household, from that family. We have a clearer picture recorded for us by the time of the temple than we do in the tabernacle because it clearly tells us that it says, “When ye enter into the land,” they had not yet entered into the land. And if we were looking at what happened at the time of the temple, there would have been a lot of buzzing, a lot of mulling around, a lot of chatter going on right outside of the temple with people probably repeating Psalm 150 and verse 1, “Praise God in His sanctuary.” Perhaps on the inside you might hear sounds of Psalm 30 being sung out, if you will, “I will extol thee, O LORD; for thou have lifted, you have lifted me up, and have not let my foes rejoice over me.” Essentially there would be some type of psalm before entering and then upon entrance, something worshipful and joyous to the Lord.
That's how they would do it. In the court of the priest, the flames would be seen dancing feverishly from the altar in a trail of smoke that would be ascending. In the court of the Israelites, a steady stream of men could be seen on the steps of the temple, presenting their offerings to the priest. So if you get the whole picture, you know, we tend to maybe have images of things, but we tend to think of the temple really does give the fullest embodiment of this, people lined up with their offerings on the steps waiting to get in. I mean that's pretty powerful if you can imagine and envision what I'm talking about. Now today's modern Judaism, Firstfruits are not offered because there is no temple. Only a ritual survives today of counting the days, perhaps marking them off on a calendar. And this is where, again, I'm going to say things that are controversial, but I'll just say them.
Because there's no temple and there's therefore no priest, but why would you not offer an offering? See, this is where I get a little bit like, okay, there's no more temple for you, but in this day and age where there's synagogues, okay, and there's places of worship, if you are going to be slaying saber-tooth tigers, right? Does everybody know what I mean when I say that? Okay, good. Because if I have to explain it, I will; I don't want anybody to go, “What the hell is she talking about, saber-toothed tigers?” They're extinct, okay? No, there's one at the back of the room. So my point is this, it's mind-boggling to me that Christians and Jews are reading the same book, and the book didn't say, “Now you'll stop.” Okay, I get it, at the fall of Jerusalem, everything ceased. But now you've got places of worship, so why, why wouldn't you do that? “Oh, because we don't live in an agrarian society anymore,” okay, but there's other ways to present Firstfruits, and we've exercised them here for probably at least 40 years.
So there's a lot of things. I don't know, is this as selective, how we're going to worship? Do we, do we engage in selectivity? How do we decide what we worship and what we don't? What we say, “Oh, we don't do that anymore. We just mark it on the calendar, but we don't do that anymore.” I don't understand. And don't, you try to understand because it won't make sense to you either. So first things, first things in general, are very important to God. If you remember, just take the passage of the children of Israel in Egypt's bondage, the firstborn.
So when we think about firsts, that's important. And the first, when I speak of Firstfruits, yes, the harvest is one, but the Firstfruits, first things, Christ coming out of the grave, I'd say, “Put these two things on a very equal plane and understand,” and this is what I think is very important. First things with God matter, and I think they still matter today. Not so much as you're firstborn versus your thirdborn, or if you; whatever it is that's first, but the concept of putting God first.
That still matters to God. See, there are things I can say to you, God has not changed. It's we who have changed, and that's a big problem because I don't think, if people are not being taught a template; that doesn't━don't be a box checker, but if you “put God first, He takes care of the rest” is a concept that basically summarizes Firstfruits. And the promise is to expect no less than what was offered could, in this case, let's say, whatever your crop was; that the rest of the crop would be likewise.
There wouldn't be bugs, it wouldn't be destroyed, it wouldn't be rotted; fill in the blanks, okay? Now in the New Testament, there are no less than seven mentions of Firstfruit, but they deal directly with Christ or with followers of Christ. So the apostle Paul spoke of Epaentus as the firstfruit of Achaia or Achaia in Romans 16:5. He also refers to a Stephanas in 1 Corinthians 16:15. And the difference, because they're both, both being referred to as the firstfruits of Achaia, but one of them is of an individual, the other is of Stephanas, of he and his household, which also must be understood like this, because a lot of it was church in the home.
So it could have meant not Stephanas and his family alone, but the church around him in his house as well. So that's ambiguous, we can't know exactly, but one is to an individual, one is a family. Paul also used the Firstfruits in referencing what was pinched from the dough to teach that if the Firstfruit is holy, then the lump is also holy. He says that in Romans 11:16. By this he means if God chose whomever He chose, say Abraham or Jacob, then the whole lump, that means the whole, all the children of Israel, let's; if we're using that reference, okay? Paul also used the term Firstfruits in relation to the Holy Spirit and the fruits that are manifested within the believer. So all of these components are important, because what they paint is a picture of the whole Christian, of what we are to be focusing on as believers. We're not to be focused on, you know, a thousand different things.
Our focus is, look unto Him, the Author and Finisher of salvation, Jesus Christ. And if we're going to talk about how that focus remains, it's kept by the Holy Spirit. The Holy Spirit helps us, guides us, teaches us, instructs us, help, helps us to even learn while we are being taught. You know, I was reading a message in my office and the message said, “I finally found you again. I lost track of you for several years.” But this person also went on to say how when they were watching, they tuned in and they tried to understand, and it was like I was speaking a foreign language, and now they've learnt more in the last six months.
And the person says in their message, “Maybe I just; it wasn't God's time yet for me.” And that's exactly it. I know because many of you are just like that. I'm like that. I've shared with you my anger. Why couldn't God have opened my eyes sooner, right? But that was part of God's plan. He knew the timing to be harvested, at least to be picked or opened up, right? Because that's what He does. He knows how to do it. We talk about the deposit of the Spirit in each believer. I just referenced as a type of Firstfruit. And much later in the book of Revelation, we'll encounter the 144 preachers of righteousness who will be sealed just prior to the opening of the seventh seal; all these numbers are important, 12,000 from each tribe sealed from God's wrath at the very start of the day of the Lord.
And that expression alone becomes important because these 144,000 will be preaching to people and there will be what we'll call a final harvest, an end harvest. That will be it. That's the final call, like you're in a bar, “Last call for alcohol,” “Last call for salvation happening right here with 144,000 peppered throughout the earth. That's it. That's your last call.” And I, I would really love for people to read that passage and don't read it like it's a cartoon or it's some caricature that maybe will happen. No, that's, that's what God said is going to happen in the future. And by the way, we're, we're far enough along in the world to see what's going on to know that most of the stuff that is being foretold of in the future, for us is coming to pass. So, I don't know, you know, when God has a pretty good track record of, of making things that he says happen, happen, you've got my attention. I don't need to be convinced or coerced into believing what is blatantly obvious.
So these 144,000 are called Firstfruit. They will be the guarantee that God has not cast away all His people or the ones that didn't answer immediately forever. But rather that God will purify the remnant, just as was prophesied by Daniel, in Daniel's seventieth week. Now I know I'm probably saying stuff that some may not be familiar with and that's okay, stick around and we'll eventually get to it. But this is how the apostle Paul makes a bold claim when he says, “All Israel will be saved.” That is in Romans 11:26. If you read that passage carefully, it makes perfect sense that he's talking about a final harvest that will occur.
It makes perfect sense to me. And I, I hate to sound redundant and repetitive, but in the book of Zechariah, it explicitly says, “They will look upon him whom they have pierced and they will mourn,” meaning they will recognize that the very Savior that they said is “A fraud, it's a lie, it's not true. And we're waiting for our Messiah who's not your Messiah” will go, “Uh-oh, my bad. He was the one all along.” Can you imagine that? I mean, I can, I actually have to feel sorry for people who have been so closed in their thinking that they couldn't read the Old and see the description of the One who came in the New.
It's Him; there aren't two Messiahs, there's only One. He was here and He's coming back and God's going to give those people who rejected Him a second chance, which is why when we read passages that talk about all the people coming to the mount to worship, again, don't think that's a caricature. Why is Israel such a big deal? For the right reasons, not all the ones that a lot of people in ministry try to make it a Zionist movement or they try; no, because the Bible says, “In this little swath of land, basically where I started I will finish.” Don't, don't get more hung up on the land or the people, and the people who are there now won't even be there, likely when He returns. And I won't tell you why either. And it has nothing to do, and it has nothing to do with the rapture either. So leave that one alone. The Firstfruits, like Israel's other springtime feasts, has its fulfillment, fulfillment in Christ's first coming, but perhaps the more important emphasis should be, but now Christ is risen from the dead, has become the Firstfruit of those who have fallen asleep.
And we know that Jesus rose from the dead━I told you I'd be repeating a lot, which I'm doing━which makes the fulfillment of that feast as it's applied to Him. Just put a period there because He did come out of the grave. The Resurrection is a guarantee of harvest of souls that will be like Christ. The fact is that there is life after death, not just we just cease being.
Daniel says something pretty profound. Remember, Daniel, he's not known for these things, but his 70 weeks and all the messages within his book are New Testament, or as New Testament as you can get. He says, “And many who sleep in the dust of the earth shall awake, some to everlasting life, some to shame, and some to everlasting contempt,” which means all. Check this out. The resurrection or the resurrected life if you will; oh, you're going to love this, all will be resurrected. All. But not all will be resurrected with Christ. Would you like me to say that again? All will be resurrected, but not all will be resurrected with Christ. Some will be resurrected to eternal damnation. That's also resurrected life that lives on in perpetuity in torment. “Oh, I don't like that.” Well, I didn't write those words, so don't, don't come complaining to me. But, you know, even Christ said something that was pretty shocking in His day.
He said, “Do not marvel for the, for the hour is coming in which all who are in their graves will hear his voice and come forth, some to resurrected life and others to condemnation.” That's John 5. So even out of the mouth of our Lord, He even says this. Don't think everybody gets a ticket and you're all going to paradise. Some are going to get a ticket to “Coffee Break's Over”; that, the ones that laughed, I know how long you've been around, okay? I know where you live. So there's always been two parts to the harvest, and there will always be two parts to the harvest, the wheat and the chaff.
And that sums it up for you. Some will inherit and receive eternal life, dwell with God forever, and some will inherit eternal punishment. And those that belong to Him, that have trusted Him, that have looked to Him their entire time of knowing Him; and that could be a day, a year, a lifetime, they will be resurrected in the same fashion, the same way as He was. So let me take a minute now to wrap this up because I'm really out of time. The main reason for preaching these messages is to demonstrate God didn't just set out in the Old to put together a whole bunch of nonsensical, ceremonial, “Now, these are these routines we do at a set time.” They were all pointing to the future.
They were all pointing to Christ. I explained to you how Christ; we talked about the Sabbath, and we are Sabbathing in Christ daily. I talked to you about the Passover when God said, “Celebrate this, basically in perpetuity as a memorial.” Well, we are, because how could you not do two things? Remember the children of Israel's deliverance out of Egypt's bondage, and then remember your own deliverance out of this world flesh and devil bondage. Now your eyes are open and you can be able to celebrate and to rejoice and to be glad in the Lord. So when I say, without, as I said earlier, without the Old Testament, we wouldn't have the full picture of why it matters.
And if you want to put kind of the exclamation mark, Paul says in Romans 8:29, essentially that we are the first, in terms of brethren or sistern, we are the first of many, the body of believers. So it becomes clear that the church of Jesus Christ must continue until the final harvest of souls comes. Now I cannot tell you how long that time will be. The Bible's very clear, no one knows the day of the hour, but there are signposts.
There are things we can see happening in the world, and wars and rumors of wars. That doesn't mean the end is here. Trust me, when there are definitive signposts along the way that must happen that will tell you the time is nearer and nearer and nearer when these things happen. Some of these have not happened yet. That's why I said to you, there's a lot of craziness going on. There's a lot of weird stuff going on.
There's a lot of scary stuff going on, but the end is not tomorrow. Don't, don't walk out here going, “Oh my God, we're doomed tomorrow, tomorrow.” It's not like that. And I'd say to you, if there's anything that should be a takeaway from this message, and I'm, I don't engage in the antics of evangelists, but if anything is a takeaway, especially for people who are not so familiar in listening to me, it would be take the time now while you have the time. The Bible says redeem the time. Take the time now to begin learning about Him, learning about who He is, His ways, His message, His words, not to study them and repeat them like a rote computer, but that His words and Christ may dwell richly in you, that when the day comes, you're not scrambling to figure out what you need to do. You know what; you've already done it, you've already taken care of business. And I'm sorry to say it like that, but just to be as colloquial as possible so there is no misunderstanding.
It is, it is truly, it confounds me that people, if, if people say, “Well, it must be in the last days,” or “It must be close,” well, then why aren't you pressing in closer with God? That's going to be the thing that keeps all of us, I hate to tell you, sane, calm, and with the clarity of vision to know what to do while the stuff is hitting the fan. So I would say to you in, in an age which people don't seem to be that concerned, the church is very important, not the building, but as the Greek calls it, a people that belong to the Lord.
And if we who are trusting Christ, and I'm going to say it this way, you know there's a Scripture that says, “Taste and see that the Lord is good.” We have been partakers of that goodness. We have tasted what the Lord has in store for those that trust Him. Then it is indeed just like the Firstfruit, we can say, “This offering of Christ stands,” in, in terms of our version of time, “as the expectancy promised,” not, “I'm not sure it's not going to happen,” for you and for me.
Put a period there. Don't be trying to figure out “How much more, what more can I do?” That's the other problem that people engage in, “What more can I do?” Now, one last footnote here and then I'm done. We have a lot of people that will give a Firstfruit offering. And listen, I'm really a strange bird when it comes to money, and I say that because I believe that when we read the New Testament there's great clarity and understanding. God does love a hilarious giver. God loves the spirit of the person; we're not just talking about money, we're talking about somebody who says, “Sure, I'll help you out.
Sure, I'll give you a hand,” that generous nature. So when I say to you, Firstfruits is not just about everything that I've talked about, but it is also about understanding, presenting the first of whatever comes into your hand, and you can't just, where, where do you give it to God? Well, you can't, but the Bible says you bring your tithes and your offerings to the storehouse, wherever you get your spiritual food. And I still believe that's a good way of saying, “I'm putting God first”" That, that's like something that, I hate to say it like this, but it actually costs you something. And I had to learn this from our good friend, Ray Sidney. He said, “You know, you shouldn't give anything away for free,” he was referring to the people in Japan, “because then they don't think it has any value.” And I thought, “That's kind of odd, but okay, if that's your, if that's your mindset.” But if you think about it in God's book, for how much it costs for God to send and give His only begotten Son, and we who take it so casually, I think the concept of Firstfruits is brilliant, because what it does is it says, you know, we don't work to get in, we don't labor in works of the flesh, but it does say, “I'm, I'm giving my first to God, which is my best and my first.” And that could be in dedicating your child, could be any number of things, but I'm not specifically talking about Firstfruits in giving right now.
And I'd say to you, there's nothing wrong with that, as long as the person's doing it for the right reasons. Don't give with strings attached. Don't give and say, “Yes, but I, I'm hoping that if I do this, this will happen.” If you're doing Firstfruits for the reason I said, which is putting God first and He takes care of the rest, then I applaud you and I think it's a good thing.
Any other motives for doing it are the wrong motives and I don't agree with them. Now, I know that's a little bit strange, the way I just worded that, but what I'm trying to tell you is, I'm the person who's known for, I think in all of ministry, there, there might only be one person that does this and it's, it's this person right here who sends back offerings to people who don't get it. And I'm talking about people who have been abusive to me in the past or they think they're going to tell me how to run the church or how to conduct or whatever. I don't want your money. We're not; this is not that type of church.
I'm not here to take your money or grab your money or do anything with your money, because it's not your money anyway; it's God's, ha, ha. But what I am saying to you is I can give you structured ideas that if they're carried out right, they, I believe are good in God's eyes and if they're carried out, like anything else, if they're carried out for the wrong reasons, like people who give to get, if that's your mindset, you're not giving to God.
You're doing some investment scheme or you're doing some trading deal with God. But if you're really giving, this is God's, the rest God lets me keep and He puts His stamp of approval on it. He blesses me for that very reason. Now, I can't tell you what else to do, but I can tell you in these feasts as we've been looking at them, I love this one in particular because going back to the whole message I just preached, it tells me if you and I have that same expectancy, like those people that took the first of their crop, and we should have that expectancy, then there's no reason in the world why whatever we face, whatever we deal with, whatever sickness comes under our dwelling, whatever pitfalls may happen, whatever this country goes to hell in a handbasket, which it's halfway there right now, but I've connected myself to God, I'm not letting go.
I'm going to be just like Jacob/Israel. I may be a little bit crippled right now, but I'll be God-damned if I let go because I know He's the only one that can take me through this. He's the only one that can take you through all of this. So wouldn't you, you'd think you'd want to do your best. In that respect the Firstfruits speaks volumes to me. I hope it speaks to you. We'll continue on with these, but for today that's my message. You have been watching me, Pastor Melissa Scott, live from Glendale, California at Faith Center.
If you would like to attend the service with us, Sunday morning at 11am, simply call 1-800-338-3030 to receive your pass. If you'd like more teaching and you would like to go straight to our website, the address is www.PastorMelissaScott.com.
As found on YouTube
Christianity Is More than a Testimony
foreign [Music] I wanted to say I appreciate letters anything that comes my way somebody taking the time to sit down and write by whatever format I don't care it means the world to me but I also take the time when I see something maybe twisted out of context to correct it so here is one this came in a letter from a King's house and King style that looks relatively new and I'm grateful for you writing me but the person says I know we are not supposed to give testimonies I never said that what I said is testimonies cannot listen what happened to me may not happen to you but in the big picture let me just say this every person who calls themselves a Christian has a testimony make no mistake about that okay if you say oh I don't have one it's because you're too busy focused on the person who stands up who says well I used to be this and now I'm that and you don't understand what it means to say a sinner saved by grace and looking at oneself we all have a testimony the reason why I am against testimony in church is because that is personal subjective to the person and my experiences are not yours so I'm not against testimony per se simply not in a public form and not added to a church service I believe all it does most of the time when people stand up and say what the Lord's done for them usually it creates a sense of well hmm the Lord didn't do that for me or I was never like that when in fact every single person who calls on the name of Jesus Christ has a testimony so I want to clear that up [Music] [Music] coming to this house
As found on YouTube
What Makes You a Christian
don't say you are a Christian don't parse words with me don't play games with me you are a Christian when you are following Christ period you're not a Christian because you come to church one day out of the year you're following Christ and following Christ doesn't necessarily mean you come to church either how's that for putting it the way it is but you're following Christ which means you are studying him and him is not a pronoun limited to one book or one half of a book it's the whole thing that's what makes you a Christian.
As found on YouTube
I Don’t Understand Yet
https://youtube.com/watch?v=GoOlWdmUX-w
foreign many people who tune in they say I'm not sure that I understand everything you said that's okay because I didn't understand everything at the first and most people tell the truth so that the world can hear when you came in you first started listening did it all make sense to you so don't think out there that you're somehow unique because you don't understand it's called tenacity to stay with the stuff until something clicks the lights come on and you actually say oh my God why didn't I see this sooner how many that that was my experience why didn't I see this sooner how unfair is that that God didn't open my eyes sooner but thank God he did [Music] [Music] coming to this house
As found on YouTube
10 Things Only Depressed People Will Understand
Narrator Hello, Psych2Goers, Did you know with the recent movement on mental health awareness over the past few years, people are gradually coming to understand more and more about matters of depression, anxiety, trauma, and other mental disorders? There’s also less stigma surrounding the need for therapy and mental health care. Nowadays, thanks to the countless public figures who have bravely spoken up about their struggles with mental illness, Do any of your favorite celebrities come to mind Still? There remains a lot unknown about the true nature of depression: the world’s most common mental illness And even more it’s, only those struggling with it. That can truly understand So with that said, here are 10 things. Only depressed people will understand the Number one difficulty with communicating your emotions Within the depths of depression. There may reside complex emotions such as sadness, hopelessness, helplessness, anger, fear, shame, and guilt. Further still, depression might manifest as an unending sense of emotional numbness and desolation, Either way. Putting your feelings into words and communicating them with others is a constant struggle when you’re depressed, especially when loved ones are asking you how you feel or how you’re doing because they suspect something is wrong. You don’t want them to worry, But when you’re in the clutches of depression, you just don’t know what or even how to tell them Number two the guilt of not having a good reason for being depressed. Well, why are you depressed? What do you even have to be depressed about? In the first place, Sound familiar, Perhaps one of the most difficult things about having depression? Is the pain of being misunderstood or judged? Do you agree? Depression needs to have a tangible reason, Though. You understand that depression is something that affects people of all ages, genders races, classes, and social backgrounds. You still can’t help but feel guilty when others judge you for not having a good reason for being depressed. Number. Three, the anger over constantly being told I understand: Do you find it hard to believe when others say they understand what you’re going through? Another thing not talked about enough when it comes to depression is how frustrating it can feel to constantly be told by others that they understand when all you want na do is tell them that unless they’ve been diagnosed with depression themselves and been inside Your mind: no, they don’t Just because they’ve felt really sad sometimes or this terrible thing happened to them once upon a time does not mean that they know how it feels to have clinical depression Number four, the pain of losing your love And passion for life: How long has it been since you picked up a paintbrush or strummed a tune? The American Psychological Association states that the defining feature of clinical depression is markedly diminished interest or pleasure in all, or most all activities Simply put. This means that when you’re suffering from depression, it’s a struggle for you to find joy or enjoyment, even in the hobbies and activities that you once loved so much It makes you lose passion for life. Depression makes you unable to feel motivated to do anything anymore, and so it robs you of even the simplest of life.’s pleasures Number five, is the frustration of not being able to just snap out of it. Have you been told that a few days of rest can cure depression? One of the many reasons why depression is such a devastating mental illness. Is that a lot of people don’t understand its true nature? They think that people who are depressed can just snap out of it or just need to think more positively. There is no built-in switch for this. Your feelings are every bit as real as they feel You’re not obligated to feel any other way just because others, don’t feel the same Number six. The compulsive desire to self-isolate. Why do counselors and therapists alike? Stress the need for those struggling with depression to have a good social support system, Even though you understand the need to be surrounded by supportive loved ones. The truth is when you’re depressed, you, ‘ll most likely feel a compulsive desire to isolate yourself from others, With no energy or motivation to engage in social interactions. You tend to prefer isolation. Constant difficulty with communicating and finding enjoyment in things leads to struggling with feelings of low self-esteem and self-worth Talking to people, and staying in touch can often feel too overwhelming. When you’re struggling with depression, triggering a need to withdraw from society in general Number. Seven people think depression is the same as sadness. Sadness is part of a healthy spectrum of human emotions and is quite normal to feel from time to time.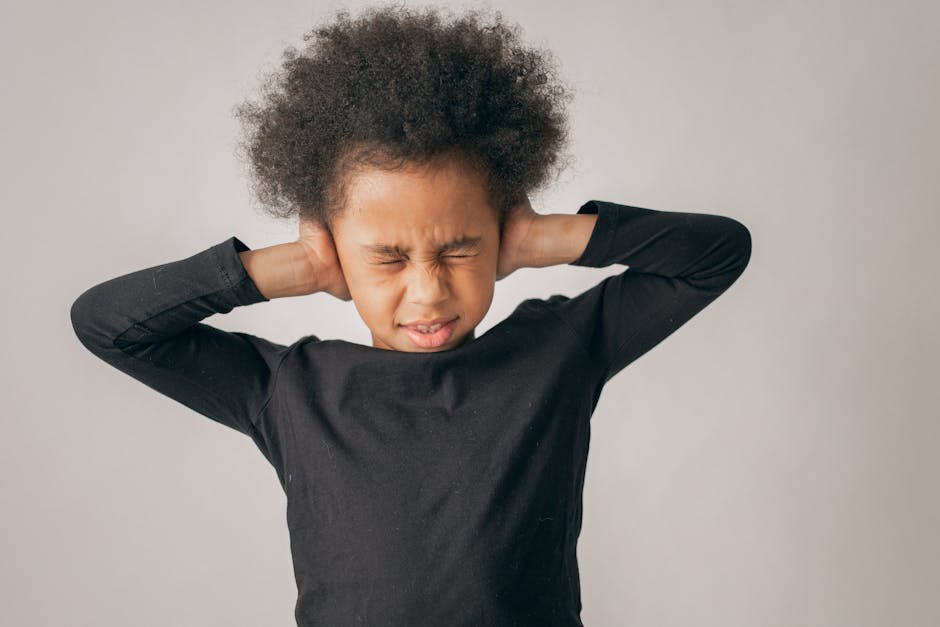  Depression, on the other hand, is a serious and debilitating mental illness that needs to be treated with professional help and therapy. These things are not all the same, and yet some people just can’t seem to grasp the difference. This can often feel very frustrating, especially when others disregard what you’re feeling as mere sadness and tell you not to think about it. Number eight people not understanding that mental illness is real. Many people still seem to think that depression is a choice and a mental illness. Isn’t real, But just because there are no physical manifestations to see doesn’t mean that the suffering you feel is not real. It’s, not just in your head. If you’re able to feel it, then it is very much real When others downplay its potency. It often leaves you feeling, as if you’re doing something wrong. As a result, you may even choose to remain silent about it. Instead, Number nine people think depression is the same for everybody Every individual’s. Experience of a mental disorder is different from Depression. Doesn’t look the same for everybody. Some people might stop eating and struggle with insomnia, while others might overeat and oversleep. Some people have high-functioning depression and may not even seem like they’re struggling at all for others, their depression might force them to lie in bed all day and do nothing. Nevertheless, all experiences of depression are valid, And number 10 learning to celebrate the little things. Finally, but perhaps most importantly, when you struggle with depression, even the littlest of victories deserve to be celebrated, Got outta bed today, smiled Managed a short conversation with someone Took the time to brush my hair, or take a bath. Give yourself a mental pat on the back. Those are all very, very important achievements for someone with depression. They might not mean much to other people, But to you struggling with mental illness on an everyday basis. They make up the good days that remind you why you need to keep fighting and why it’s so important to keep holding on It.’s important to remember not to allow others to dictate how you should feel Just because others are not feeling the same does not make it any less real. There’s no need to cover up or force yourself to change these feelings. The fact that you’re feeling it is reason enough to validate it If you are struggling with depression or any other mental illness. Please know that there is always hope and help and that someday things can be better. Seeking professional help can help you on the road to improvement, Leave a comment down below about your experience with depression. If you’d, like, Please, feel free to share any thoughts you have as well, If you found this video helpful, be sure to hit the like button and share it with those out there needing to hear this, Don’t forget to subscribe to Psych2Go and Hit the notification bell for more new videos And, as always thanks so much for watching We’ll see you next time..
Depression, on the other hand, is a serious and debilitating mental illness that needs to be treated with professional help and therapy. These things are not all the same, and yet some people just can’t seem to grasp the difference. This can often feel very frustrating, especially when others disregard what you’re feeling as mere sadness and tell you not to think about it. Number eight people not understanding that mental illness is real. Many people still seem to think that depression is a choice and a mental illness. Isn’t real, But just because there are no physical manifestations to see doesn’t mean that the suffering you feel is not real. It’s, not just in your head. If you’re able to feel it, then it is very much real When others downplay its potency. It often leaves you feeling, as if you’re doing something wrong. As a result, you may even choose to remain silent about it. Instead, Number nine people think depression is the same for everybody Every individual’s. Experience of a mental disorder is different from Depression. Doesn’t look the same for everybody. Some people might stop eating and struggle with insomnia, while others might overeat and oversleep. Some people have high-functioning depression and may not even seem like they’re struggling at all for others, their depression might force them to lie in bed all day and do nothing. Nevertheless, all experiences of depression are valid, And number 10 learning to celebrate the little things. Finally, but perhaps most importantly, when you struggle with depression, even the littlest of victories deserve to be celebrated, Got outta bed today, smiled Managed a short conversation with someone Took the time to brush my hair, or take a bath. Give yourself a mental pat on the back. Those are all very, very important achievements for someone with depression. They might not mean much to other people, But to you struggling with mental illness on an everyday basis. They make up the good days that remind you why you need to keep fighting and why it’s so important to keep holding on It.’s important to remember not to allow others to dictate how you should feel Just because others are not feeling the same does not make it any less real. There’s no need to cover up or force yourself to change these feelings. The fact that you’re feeling it is reason enough to validate it If you are struggling with depression or any other mental illness. Please know that there is always hope and help and that someday things can be better. Seeking professional help can help you on the road to improvement, Leave a comment down below about your experience with depression. If you’d, like, Please, feel free to share any thoughts you have as well, If you found this video helpful, be sure to hit the like button and share it with those out there needing to hear this, Don’t forget to subscribe to Psych2Go and Hit the notification bell for more new videos And, as always thanks so much for watching We’ll see you next time.. As found on YouTubeSeanCooper🗯 The Shyness & Social Guy ⇝ The 3 WORST Mistakes You Must AVOID If You Want To Overcome Shyness (PLUS: 1 weird trick that targets the root biological cause of shyness so you can stop being nervous, awkward, and quiet around people…) By Sean Cooper, The Shyness & Social Anxiety Guy. The fact that you’re reading this article tells me you may have already reached a point where you feel your shyness is NOT going away on its own… or you fear it’s getting worse and worse. And I don’t want you to waste one more day living a life where you feel left out, bored, or depressed because you don’t have the relationships which would make you happy. That’s why I’ve put together this page to help you avoid the worst mistakes that keep many people stuck with shyness for years… http://flywait.darekw.hop.clickbank.net/ often giving up hope of ever improving as you watch other people have interesting “normal” lives without you. Yet this doesn’t have to happen.Have a great day,
яαℓρн ℓєαмαи
As found on YouTubeSeanCooper🗯 The Shyness & Social Guy ⇝ The 3 WORST Mistakes You Must AVOID If You Want To Overcome Shyness (PLUS: 1 weird trick that targets the root biological cause of shyness so you can stop being nervous, awkward, and quiet around people…) By Sean Cooper, The Shyness & Social Anxiety Guy. The fact that you’re reading this article tells me you may have already reached a point where you feel your shyness is NOT going away on its own… or you fear it’s getting worse and worse. And I don’t want you to waste one more day living a life where you feel left out, bored, or depressed because you don’t have the relationships which would make you happy. That’s why I’ve put together this page to help you avoid the worst mistakes that keep many people stuck with shyness for years… http://flywait.darekw.hop.clickbank.net/ often giving up hope of ever improving as you watch other people have interesting “normal” lives without you. Yet this doesn’t have to happen.Have a great day,
яαℓρн ℓєαмαи
 Depression, on the other hand, is a serious and debilitating mental illness that needs to be treated with professional help and therapy. These things are not all the same, and yet some people just can’t seem to grasp the difference. This can often feel very frustrating, especially when others disregard what you’re feeling as mere sadness and tell you not to think about it. Number eight people not understanding that mental illness is real. Many people still seem to think that depression is a choice and a mental illness. Isn’t real, But just because there are no physical manifestations to see doesn’t mean that the suffering you feel is not real. It’s, not just in your head. If you’re able to feel it, then it is very much real When others downplay its potency. It often leaves you feeling, as if you’re doing something wrong. As a result, you may even choose to remain silent about it. Instead, Number nine people think depression is the same for everybody Every individual’s. Experience of a mental disorder is different from Depression. Doesn’t look the same for everybody. Some people might stop eating and struggle with insomnia, while others might overeat and oversleep. Some people have high-functioning depression and may not even seem like they’re struggling at all for others, their depression might force them to lie in bed all day and do nothing. Nevertheless, all experiences of depression are valid, And number 10 learning to celebrate the little things. Finally, but perhaps most importantly, when you struggle with depression, even the littlest of victories deserve to be celebrated, Got outta bed today, smiled Managed a short conversation with someone Took the time to brush my hair, or take a bath. Give yourself a mental pat on the back. Those are all very, very important achievements for someone with depression. They might not mean much to other people, But to you struggling with mental illness on an everyday basis. They make up the good days that remind you why you need to keep fighting and why it’s so important to keep holding on It.’s important to remember not to allow others to dictate how you should feel Just because others are not feeling the same does not make it any less real. There’s no need to cover up or force yourself to change these feelings. The fact that you’re feeling it is reason enough to validate it If you are struggling with depression or any other mental illness. Please know that there is always hope and help and that someday things can be better. Seeking professional help can help you on the road to improvement, Leave a comment down below about your experience with depression. If you’d, like, Please, feel free to share any thoughts you have as well, If you found this video helpful, be sure to hit the like button and share it with those out there needing to hear this, Don’t forget to subscribe to Psych2Go and Hit the notification bell for more new videos And, as always thanks so much for watching We’ll see you next time..
Depression, on the other hand, is a serious and debilitating mental illness that needs to be treated with professional help and therapy. These things are not all the same, and yet some people just can’t seem to grasp the difference. This can often feel very frustrating, especially when others disregard what you’re feeling as mere sadness and tell you not to think about it. Number eight people not understanding that mental illness is real. Many people still seem to think that depression is a choice and a mental illness. Isn’t real, But just because there are no physical manifestations to see doesn’t mean that the suffering you feel is not real. It’s, not just in your head. If you’re able to feel it, then it is very much real When others downplay its potency. It often leaves you feeling, as if you’re doing something wrong. As a result, you may even choose to remain silent about it. Instead, Number nine people think depression is the same for everybody Every individual’s. Experience of a mental disorder is different from Depression. Doesn’t look the same for everybody. Some people might stop eating and struggle with insomnia, while others might overeat and oversleep. Some people have high-functioning depression and may not even seem like they’re struggling at all for others, their depression might force them to lie in bed all day and do nothing. Nevertheless, all experiences of depression are valid, And number 10 learning to celebrate the little things. Finally, but perhaps most importantly, when you struggle with depression, even the littlest of victories deserve to be celebrated, Got outta bed today, smiled Managed a short conversation with someone Took the time to brush my hair, or take a bath. Give yourself a mental pat on the back. Those are all very, very important achievements for someone with depression. They might not mean much to other people, But to you struggling with mental illness on an everyday basis. They make up the good days that remind you why you need to keep fighting and why it’s so important to keep holding on It.’s important to remember not to allow others to dictate how you should feel Just because others are not feeling the same does not make it any less real. There’s no need to cover up or force yourself to change these feelings. The fact that you’re feeling it is reason enough to validate it If you are struggling with depression or any other mental illness. Please know that there is always hope and help and that someday things can be better. Seeking professional help can help you on the road to improvement, Leave a comment down below about your experience with depression. If you’d, like, Please, feel free to share any thoughts you have as well, If you found this video helpful, be sure to hit the like button and share it with those out there needing to hear this, Don’t forget to subscribe to Psych2Go and Hit the notification bell for more new videos And, as always thanks so much for watching We’ll see you next time.. As found on YouTubeSeanCooper🗯 The Shyness & Social Guy ⇝ The 3 WORST Mistakes You Must AVOID If You Want To Overcome Shyness (PLUS: 1 weird trick that targets the root biological cause of shyness so you can stop being nervous, awkward, and quiet around people…) By Sean Cooper, The Shyness & Social Anxiety Guy. The fact that you’re reading this article tells me you may have already reached a point where you feel your shyness is NOT going away on its own… or you fear it’s getting worse and worse. And I don’t want you to waste one more day living a life where you feel left out, bored, or depressed because you don’t have the relationships which would make you happy. That’s why I’ve put together this page to help you avoid the worst mistakes that keep many people stuck with shyness for years… http://flywait.darekw.hop.clickbank.net/ often giving up hope of ever improving as you watch other people have interesting “normal” lives without you. Yet this doesn’t have to happen.Have a great day,
яαℓρн ℓєαмαи
As found on YouTubeSeanCooper🗯 The Shyness & Social Guy ⇝ The 3 WORST Mistakes You Must AVOID If You Want To Overcome Shyness (PLUS: 1 weird trick that targets the root biological cause of shyness so you can stop being nervous, awkward, and quiet around people…) By Sean Cooper, The Shyness & Social Anxiety Guy. The fact that you’re reading this article tells me you may have already reached a point where you feel your shyness is NOT going away on its own… or you fear it’s getting worse and worse. And I don’t want you to waste one more day living a life where you feel left out, bored, or depressed because you don’t have the relationships which would make you happy. That’s why I’ve put together this page to help you avoid the worst mistakes that keep many people stuck with shyness for years… http://flywait.darekw.hop.clickbank.net/ often giving up hope of ever improving as you watch other people have interesting “normal” lives without you. Yet this doesn’t have to happen.Have a great day,
яαℓρн ℓєαмαи
The Difference Between ADHD and Anxiety Signs
– Hey, Psych2Goers. Do you have trouble paying attention? For example, zoning out
while watching this video? Do you think you have
ADHD because of this? Oftentimes, people mistake
symptoms of anxiety for ADHD because of some of the
similar traits they share. According to the Centers
for Disease Control and Prevention data, about 3 in 10 children
with ADHD have anxiety. So to help you get a better understanding of the difference
between ADHD and anxiety, here are six signs to look out for. Number one, you have poor focus because of worrying thoughts. Are you always distracted by your worries, so much so that you’re unable to focus on the things you’re doing? When fear and apprehension
dominate your thoughts, it may cause you to become restless and have trouble with sitting
still, paying attention, or staying focused in class. According to John Waldrop, MD from Weill Cornell Medical College, when you experience anxiety, your prefrontal cortex, the part of the brain which is essential for thinking, learning, and
remembering, is shut down. Your brain is concentrated
on staying safe. In contrast with ADHD, you aren’t consumed by worrying thoughts. Instead, it has more
to do with an imbalance in your hormones: dopamine
and norepinephrine, which causes you to be distracted. Number two, you don’t tend to have as many problems with impulsivity. Do you often find yourself
speaking out loud in class without raising your hand? Perhaps you were even labeled
as the troublemaker in school because of the way you
can never sit still. According to Dr. John, a
person with ADHD may feel as if there are dozens of controllers trying to control their
brains at the same time without checking in with each other first. So if you find that you
don’t appear to have as many problems with impulsivity but just struggle to speak up or stand up because of your nerves, then you may have anxiety rather than ADHD. Number three, you have trouble
completing your schoolwork because of perfectionism. Do you have trouble
completing your schoolwork? Perhaps you find yourself procrastinating even if you only have just
one assignment to you. This struggle could be because
you have so many points you wanna make in so many
ways to phrase the words that it leaves you wanting
to throw up your hands and ignore them. You’re avoiding starting your assignments because you can’t have
them be less than perfect. If you can relate to this, then it’s more likely you’re struggling with anxiety and not ADHD.  Dr. John stated that
while people with ADHD may experience difficulty
completing their schoolwork or performing tasks, it’s often due to trouble
with concentration rather than perfectionism. Number four, you are
generally more sensitive to social cues. Are you very sensitive to how you come across to other people? Do you find yourself often uncomfortable with your social environment? Perhaps you find it challenging to eat in front of other people or tend to avoid speaking in public because of an overwhelming fear that people will judge you negatively. According to Dr. John,
if your answers are yes to the above questions, it’s more likely that you
have anxiety rather than ADHD. This is because people
with ADHD usually struggle with understanding or missing social cues rather than being hypersensitive to them. Number five, you experience
a racing heart, clamminess, tense muscles, headaches,
nausea, or dizziness. Do you often experience
headaches, nausea, or dizziness? These are just some of
the symptoms of anxiety. Dr. John stated that anxiety comes from a tiny almond-shaped part at the back of your brain
called the amygdala. As a watchman for your brain, it is constantly watching out for danger. And whenever it detects danger, it triggers a fight or flight response. However, for anxious people, the amygdala is large and hypersensitive. Because of this, it ends up sending out
a lot of false alarms. You can think of it as a watchman
who cries wolf too often. As a result, your brain may sense threats even in non-threatening situations. And number six, you are unlikely
to show problem behaviors when you’re feeling calm, safe,
and doing things you enjoy. How do you act when you’re having fun? Whether it’s listening
to your favorite music or playing video games, you
may find yourself feeling calm and safe while doing the things
that you genuinely enjoy. You are neither restless nor feeling like you need
to catch your breath. According to Dr. John, anxious
individuals are unlikely to display any problem behaviors
when feeling calm and safe and doing something they enjoy. On the contrary, people with ADHD will experience problem behaviors even when they engage in a particular fun or exciting activity.
Dr. John stated that
while people with ADHD may experience difficulty
completing their schoolwork or performing tasks, it’s often due to trouble
with concentration rather than perfectionism. Number four, you are
generally more sensitive to social cues. Are you very sensitive to how you come across to other people? Do you find yourself often uncomfortable with your social environment? Perhaps you find it challenging to eat in front of other people or tend to avoid speaking in public because of an overwhelming fear that people will judge you negatively. According to Dr. John,
if your answers are yes to the above questions, it’s more likely that you
have anxiety rather than ADHD. This is because people
with ADHD usually struggle with understanding or missing social cues rather than being hypersensitive to them. Number five, you experience
a racing heart, clamminess, tense muscles, headaches,
nausea, or dizziness. Do you often experience
headaches, nausea, or dizziness? These are just some of
the symptoms of anxiety. Dr. John stated that anxiety comes from a tiny almond-shaped part at the back of your brain
called the amygdala. As a watchman for your brain, it is constantly watching out for danger. And whenever it detects danger, it triggers a fight or flight response. However, for anxious people, the amygdala is large and hypersensitive. Because of this, it ends up sending out
a lot of false alarms. You can think of it as a watchman
who cries wolf too often. As a result, your brain may sense threats even in non-threatening situations. And number six, you are unlikely
to show problem behaviors when you’re feeling calm, safe,
and doing things you enjoy. How do you act when you’re having fun? Whether it’s listening
to your favorite music or playing video games, you
may find yourself feeling calm and safe while doing the things
that you genuinely enjoy. You are neither restless nor feeling like you need
to catch your breath. According to Dr. John, anxious
individuals are unlikely to display any problem behaviors
when feeling calm and safe and doing something they enjoy. On the contrary, people with ADHD will experience problem behaviors even when they engage in a particular fun or exciting activity. For example, a person with ADHD may become so engrossed
with painting a picture that they tune out or completely
ignore everything else. This behavior is known as hyperfocus. Did you relate to any of
the signs we’ve mentioned? Let us know in the comments below. If you found this video helpful, be sure to like, subscribe,
and share this video with those who might benefit from it. And don’t forget to hit
the notification bell icon to get notified whenever
Psych2Go posts a new video. As always, the references and
studies used in this video are added in the description below. Thanks so much for watching
and see you in our next video. (light music).As found on YouTubeSeanCooper🗯 The Shyness & Social Guy ⇝ The 3 WORST Mistakes You Must AVOID If You Want To Overcome Shyness (PLUS: 1 weird trick that targets the root biological cause of shyness so you can stop being nervous, awkward, and quiet around people…) By Sean Cooper, The Shyness & Social Anxiety Guy. The fact that you’re reading this article tells me you may have already reached a point where you feel your shyness is NOT going away on its own… or you fear it’s getting worse and worse. And I don’t want you to waste one more day living a life where you feel left out, bored, or depressed because you don’t have the relationships which would make you happy. That’s why I’ve put together this page to help you avoid the worst mistakes that keep many people stuck with shyness for years… http://flywait.darekw.hop.clickbank.net/ often giving up hope of ever improving as you watch other people have interesting “normal” lives without you. Yet this doesn’t have to happen.
For example, a person with ADHD may become so engrossed
with painting a picture that they tune out or completely
ignore everything else. This behavior is known as hyperfocus. Did you relate to any of
the signs we’ve mentioned? Let us know in the comments below. If you found this video helpful, be sure to like, subscribe,
and share this video with those who might benefit from it. And don’t forget to hit
the notification bell icon to get notified whenever
Psych2Go posts a new video. As always, the references and
studies used in this video are added in the description below. Thanks so much for watching
and see you in our next video. (light music).As found on YouTubeSeanCooper🗯 The Shyness & Social Guy ⇝ The 3 WORST Mistakes You Must AVOID If You Want To Overcome Shyness (PLUS: 1 weird trick that targets the root biological cause of shyness so you can stop being nervous, awkward, and quiet around people…) By Sean Cooper, The Shyness & Social Anxiety Guy. The fact that you’re reading this article tells me you may have already reached a point where you feel your shyness is NOT going away on its own… or you fear it’s getting worse and worse. And I don’t want you to waste one more day living a life where you feel left out, bored, or depressed because you don’t have the relationships which would make you happy. That’s why I’ve put together this page to help you avoid the worst mistakes that keep many people stuck with shyness for years… http://flywait.darekw.hop.clickbank.net/ often giving up hope of ever improving as you watch other people have interesting “normal” lives without you. Yet this doesn’t have to happen.
 Dr. John stated that
while people with ADHD may experience difficulty
completing their schoolwork or performing tasks, it’s often due to trouble
with concentration rather than perfectionism. Number four, you are
generally more sensitive to social cues. Are you very sensitive to how you come across to other people? Do you find yourself often uncomfortable with your social environment? Perhaps you find it challenging to eat in front of other people or tend to avoid speaking in public because of an overwhelming fear that people will judge you negatively. According to Dr. John,
if your answers are yes to the above questions, it’s more likely that you
have anxiety rather than ADHD. This is because people
with ADHD usually struggle with understanding or missing social cues rather than being hypersensitive to them. Number five, you experience
a racing heart, clamminess, tense muscles, headaches,
nausea, or dizziness. Do you often experience
headaches, nausea, or dizziness? These are just some of
the symptoms of anxiety. Dr. John stated that anxiety comes from a tiny almond-shaped part at the back of your brain
called the amygdala. As a watchman for your brain, it is constantly watching out for danger. And whenever it detects danger, it triggers a fight or flight response. However, for anxious people, the amygdala is large and hypersensitive. Because of this, it ends up sending out
a lot of false alarms. You can think of it as a watchman
who cries wolf too often. As a result, your brain may sense threats even in non-threatening situations. And number six, you are unlikely
to show problem behaviors when you’re feeling calm, safe,
and doing things you enjoy. How do you act when you’re having fun? Whether it’s listening
to your favorite music or playing video games, you
may find yourself feeling calm and safe while doing the things
that you genuinely enjoy. You are neither restless nor feeling like you need
to catch your breath. According to Dr. John, anxious
individuals are unlikely to display any problem behaviors
when feeling calm and safe and doing something they enjoy. On the contrary, people with ADHD will experience problem behaviors even when they engage in a particular fun or exciting activity.
Dr. John stated that
while people with ADHD may experience difficulty
completing their schoolwork or performing tasks, it’s often due to trouble
with concentration rather than perfectionism. Number four, you are
generally more sensitive to social cues. Are you very sensitive to how you come across to other people? Do you find yourself often uncomfortable with your social environment? Perhaps you find it challenging to eat in front of other people or tend to avoid speaking in public because of an overwhelming fear that people will judge you negatively. According to Dr. John,
if your answers are yes to the above questions, it’s more likely that you
have anxiety rather than ADHD. This is because people
with ADHD usually struggle with understanding or missing social cues rather than being hypersensitive to them. Number five, you experience
a racing heart, clamminess, tense muscles, headaches,
nausea, or dizziness. Do you often experience
headaches, nausea, or dizziness? These are just some of
the symptoms of anxiety. Dr. John stated that anxiety comes from a tiny almond-shaped part at the back of your brain
called the amygdala. As a watchman for your brain, it is constantly watching out for danger. And whenever it detects danger, it triggers a fight or flight response. However, for anxious people, the amygdala is large and hypersensitive. Because of this, it ends up sending out
a lot of false alarms. You can think of it as a watchman
who cries wolf too often. As a result, your brain may sense threats even in non-threatening situations. And number six, you are unlikely
to show problem behaviors when you’re feeling calm, safe,
and doing things you enjoy. How do you act when you’re having fun? Whether it’s listening
to your favorite music or playing video games, you
may find yourself feeling calm and safe while doing the things
that you genuinely enjoy. You are neither restless nor feeling like you need
to catch your breath. According to Dr. John, anxious
individuals are unlikely to display any problem behaviors
when feeling calm and safe and doing something they enjoy. On the contrary, people with ADHD will experience problem behaviors even when they engage in a particular fun or exciting activity. For example, a person with ADHD may become so engrossed
with painting a picture that they tune out or completely
ignore everything else. This behavior is known as hyperfocus. Did you relate to any of
the signs we’ve mentioned? Let us know in the comments below. If you found this video helpful, be sure to like, subscribe,
and share this video with those who might benefit from it. And don’t forget to hit
the notification bell icon to get notified whenever
Psych2Go posts a new video. As always, the references and
studies used in this video are added in the description below. Thanks so much for watching
and see you in our next video. (light music).As found on YouTubeSeanCooper🗯 The Shyness & Social Guy ⇝ The 3 WORST Mistakes You Must AVOID If You Want To Overcome Shyness (PLUS: 1 weird trick that targets the root biological cause of shyness so you can stop being nervous, awkward, and quiet around people…) By Sean Cooper, The Shyness & Social Anxiety Guy. The fact that you’re reading this article tells me you may have already reached a point where you feel your shyness is NOT going away on its own… or you fear it’s getting worse and worse. And I don’t want you to waste one more day living a life where you feel left out, bored, or depressed because you don’t have the relationships which would make you happy. That’s why I’ve put together this page to help you avoid the worst mistakes that keep many people stuck with shyness for years… http://flywait.darekw.hop.clickbank.net/ often giving up hope of ever improving as you watch other people have interesting “normal” lives without you. Yet this doesn’t have to happen.
For example, a person with ADHD may become so engrossed
with painting a picture that they tune out or completely
ignore everything else. This behavior is known as hyperfocus. Did you relate to any of
the signs we’ve mentioned? Let us know in the comments below. If you found this video helpful, be sure to like, subscribe,
and share this video with those who might benefit from it. And don’t forget to hit
the notification bell icon to get notified whenever
Psych2Go posts a new video. As always, the references and
studies used in this video are added in the description below. Thanks so much for watching
and see you in our next video. (light music).As found on YouTubeSeanCooper🗯 The Shyness & Social Guy ⇝ The 3 WORST Mistakes You Must AVOID If You Want To Overcome Shyness (PLUS: 1 weird trick that targets the root biological cause of shyness so you can stop being nervous, awkward, and quiet around people…) By Sean Cooper, The Shyness & Social Anxiety Guy. The fact that you’re reading this article tells me you may have already reached a point where you feel your shyness is NOT going away on its own… or you fear it’s getting worse and worse. And I don’t want you to waste one more day living a life where you feel left out, bored, or depressed because you don’t have the relationships which would make you happy. That’s why I’ve put together this page to help you avoid the worst mistakes that keep many people stuck with shyness for years… http://flywait.darekw.hop.clickbank.net/ often giving up hope of ever improving as you watch other people have interesting “normal” lives without you. Yet this doesn’t have to happen.9 Uncomfortable Signs You’re Healing Emotionally
Narrator, Hey Psych2Goers, welcome back to another video Healing is not easy. There’s a lot of stigma regarding going to therapy and doing any independent inner self-work. It’s still seen as something that either weak or crazy people do, and that’s – just not true, It might not be 100 easy, but healing is a journey that leads to deep fulfillment that nothing outside of you could shake or take away. This process is very humbling, but with high risk comes high reward. During this journey, you will start to feel the growing pains of change and self-integration Keep moving forward. This discomfort is helping you move into a beautiful life in which you have a deeper sense of inner peace. Here are nine uncomfortable signs that you are healing Number one. You allow yourself to feel your emotions When you’re still stuck in survival mode. You are mostly focused on logic and what you see because emotions are painful for you to feel and process It’s hard for you to take the time and make room for your emotions to just be acknowledged and validated because it reminds you of the hurt that You would’ve liked to keep buried When you heal. You start acknowledging your negative and positive emotions because you realize that extreme focus on one is detrimental to your whole being and that you are a whole person. It’s uncomfortable at first, but as you are no longer suppressing or denying them, you see the value of your emotions and feelings and of just letting yourself sit with them and allowing them to pass Number Two. You’re getting better at expressing and maintaining boundaries When you’re not healed or in the process, you struggle with stating and enforcing boundaries because you’re afraid of rejection, feelings of shame and guilt from putting your interest first or saying what’s on your mind, It’s unusual to set firm boundaries when you’re not used to it, but once you start, it creates more healthy interpersonal dynamics, because you stated your opinions and emotions. You have the mental and emotional clarity and you are more capable of making your decisions Number three. You accept that you’ve, been through difficult experiences. Life is hard and unfair, and instead of suppressing all of the experiences that you have been through, you acknowledge and accept that they happened. You accept that these people’s place and things had a life-changing impact on you and probably still do Once. You have accepted that these uncomfortable events impacted you in their entirety. They start to hurt you less because you’ve accepted the truth and are in charge of the narrative of your life again Number four, you’re, less reactive and more responsive. When you’re in survival mode, Everything and everyone is a threat and is treated as such. Nothing is trusted and you, don’t have time to sit and logically think things through, because you are pure action needing to defend yourself constantly. Once you start healing your natural response of lashing out shutting down, running away, or people-pleasing is tested and slowly makes way for questioning your feelings and reactions. Regarding things, You even find yourself asking. Why do I think this way? Where does this thinking come from? You start practicing emotional self-regulation, self-analysis, and responsibility. Number five you realize that healing is not linear Healing is uncomfortable because you are unearthing and confronting things you would’ve preferred to keep suppressed. Once you get into the rhythm, you realize that part of that healing is that this distress is okay and normal, because it’s not a straight road to inner peace and healing You understand and has experienced the highs and lows of healing and know that the feeling of today will not match the feelings of tomorrow or even later, on Number six. You begin to step out of your comfort zone Here,’s the thing about healing It:’s, not something everyone will do.  However, if you decide to it has far-reaching benefits beyond the acceptance and acknowledgment of the traumatic experience Once you are in the healing process, you are developing bravery around your emotions and your mind With this newfound conscious control. You are no longer scared by things that scared you before Scared of making a living situation change. You now are redecorating your bedroom and experimenting with paint colors. You never thought you would Go to a party you don’t know Before you would’ve recoiled at the thought, but now it’s a little less anxiety-inducing and you have a bit more confidence Number seven. You easily accept disappointments and take them in stride. Life is a balance of success and failure, light and dark ups and downs. When you’re not healing disappointments hit, you like a freight truck to the chest, knocking all of the motivation and passion out of you With healing you understand that bad days do happen and can’t be avoided, but are also temporary Any disappointments or unmet Expectations are accepted and taken in stride. You respond in better healthier ways that are less reactive Number. Eight you have more inner peace Healing brings about self-integration. If you’re a Harry Potter, fan it’s as if Voldemort brought back all of his Horcruxes and decided on becoming a better complete person who accepts the natural way of life on a soul level. And if you’re, not a fan. It’s like taking inventory of all of your experiences painful or not, and seeing yourself as the whole person You develop this inner peace because you deeply forgive yourself and you can readily forgive others too. By having this peace and integration, you are less likely to self-sabotage because you’re no longer a warring country within yourself with conflicting desires and emotions. You reconcile your inner differences. You no longer criticize and dismantle your character in your mind And number nine. You welcome help and support The independent survivor. Has a don’t ask for help mentality, maybe because they never got it when they needed it or because of the harsh rejection when they spoke up, They shut down to get by and decided to do it by themselves because they had no choice With healing You start to realize that as strong as you are, you can’t carry and do everything by yourself. You do need help and we all do and it’s available out there for you. You are more open to support and less afraid of having this need for assistance met. The pride and shame you might feel for asking for help are gone, because you know that it’s, okay, to let go of the heavy burden on your shoulders and have someone to lean on. Did you relate to any of these points? Do you feel that you are beginning to heal As rewarding as the first step of healing? You will run into the discomfort of your healing and this will try to make you stop to lessen or ignore the pain, but whatever you resist you prolong. If you are in the healing process, well done, I’m proud of you for doing this work and I hope you can find peace through it And if you’re not that’s, okay, because healing is a long process that takes time you’re still living and doing what you can Applaud yourselves. Did you find this video valuable, Tell us in the comments below Please like and share it with friends that might find use in this video too, and make sure to subscribe to Psych2Go and hit the notification bell for more content. All the references used are added in the description box below. Thank you for watching and see you next time…As found on YouTubeSeanCooper🗯 The Shyness & Social Guy ⇝ The 3 WORST Mistakes You Must AVOID If You Want To Overcome Shyness (PLUS: 1 weird trick that targets the root biological cause of shyness so you can stop being nervous, awkward, and quiet around people…) By Sean Cooper, The Shyness & Social Anxiety Guy. The fact that you’re reading this article tells me you may have already reached a point where you feel your shyness is NOT going away on its own… or you fear it’s getting worse and worse. And I don’t want you to waste one more day living a life where you feel left out, bored, or depressed because you don’t have the relationships which would make you happy. That’s why I’ve put together this page to help you avoid the worst mistakes that keep many people stuck with shyness for years… http://flywait.darekw.hop.clickbank.net/ often giving up hope of ever improving as you watch other people have interesting “normal” lives without you. Yet this doesn’t have to happen.
However, if you decide to it has far-reaching benefits beyond the acceptance and acknowledgment of the traumatic experience Once you are in the healing process, you are developing bravery around your emotions and your mind With this newfound conscious control. You are no longer scared by things that scared you before Scared of making a living situation change. You now are redecorating your bedroom and experimenting with paint colors. You never thought you would Go to a party you don’t know Before you would’ve recoiled at the thought, but now it’s a little less anxiety-inducing and you have a bit more confidence Number seven. You easily accept disappointments and take them in stride. Life is a balance of success and failure, light and dark ups and downs. When you’re not healing disappointments hit, you like a freight truck to the chest, knocking all of the motivation and passion out of you With healing you understand that bad days do happen and can’t be avoided, but are also temporary Any disappointments or unmet Expectations are accepted and taken in stride. You respond in better healthier ways that are less reactive Number. Eight you have more inner peace Healing brings about self-integration. If you’re a Harry Potter, fan it’s as if Voldemort brought back all of his Horcruxes and decided on becoming a better complete person who accepts the natural way of life on a soul level. And if you’re, not a fan. It’s like taking inventory of all of your experiences painful or not, and seeing yourself as the whole person You develop this inner peace because you deeply forgive yourself and you can readily forgive others too. By having this peace and integration, you are less likely to self-sabotage because you’re no longer a warring country within yourself with conflicting desires and emotions. You reconcile your inner differences. You no longer criticize and dismantle your character in your mind And number nine. You welcome help and support The independent survivor. Has a don’t ask for help mentality, maybe because they never got it when they needed it or because of the harsh rejection when they spoke up, They shut down to get by and decided to do it by themselves because they had no choice With healing You start to realize that as strong as you are, you can’t carry and do everything by yourself. You do need help and we all do and it’s available out there for you. You are more open to support and less afraid of having this need for assistance met. The pride and shame you might feel for asking for help are gone, because you know that it’s, okay, to let go of the heavy burden on your shoulders and have someone to lean on. Did you relate to any of these points? Do you feel that you are beginning to heal As rewarding as the first step of healing? You will run into the discomfort of your healing and this will try to make you stop to lessen or ignore the pain, but whatever you resist you prolong. If you are in the healing process, well done, I’m proud of you for doing this work and I hope you can find peace through it And if you’re not that’s, okay, because healing is a long process that takes time you’re still living and doing what you can Applaud yourselves. Did you find this video valuable, Tell us in the comments below Please like and share it with friends that might find use in this video too, and make sure to subscribe to Psych2Go and hit the notification bell for more content. All the references used are added in the description box below. Thank you for watching and see you next time…As found on YouTubeSeanCooper🗯 The Shyness & Social Guy ⇝ The 3 WORST Mistakes You Must AVOID If You Want To Overcome Shyness (PLUS: 1 weird trick that targets the root biological cause of shyness so you can stop being nervous, awkward, and quiet around people…) By Sean Cooper, The Shyness & Social Anxiety Guy. The fact that you’re reading this article tells me you may have already reached a point where you feel your shyness is NOT going away on its own… or you fear it’s getting worse and worse. And I don’t want you to waste one more day living a life where you feel left out, bored, or depressed because you don’t have the relationships which would make you happy. That’s why I’ve put together this page to help you avoid the worst mistakes that keep many people stuck with shyness for years… http://flywait.darekw.hop.clickbank.net/ often giving up hope of ever improving as you watch other people have interesting “normal” lives without you. Yet this doesn’t have to happen.
 However, if you decide to it has far-reaching benefits beyond the acceptance and acknowledgment of the traumatic experience Once you are in the healing process, you are developing bravery around your emotions and your mind With this newfound conscious control. You are no longer scared by things that scared you before Scared of making a living situation change. You now are redecorating your bedroom and experimenting with paint colors. You never thought you would Go to a party you don’t know Before you would’ve recoiled at the thought, but now it’s a little less anxiety-inducing and you have a bit more confidence Number seven. You easily accept disappointments and take them in stride. Life is a balance of success and failure, light and dark ups and downs. When you’re not healing disappointments hit, you like a freight truck to the chest, knocking all of the motivation and passion out of you With healing you understand that bad days do happen and can’t be avoided, but are also temporary Any disappointments or unmet Expectations are accepted and taken in stride. You respond in better healthier ways that are less reactive Number. Eight you have more inner peace Healing brings about self-integration. If you’re a Harry Potter, fan it’s as if Voldemort brought back all of his Horcruxes and decided on becoming a better complete person who accepts the natural way of life on a soul level. And if you’re, not a fan. It’s like taking inventory of all of your experiences painful or not, and seeing yourself as the whole person You develop this inner peace because you deeply forgive yourself and you can readily forgive others too. By having this peace and integration, you are less likely to self-sabotage because you’re no longer a warring country within yourself with conflicting desires and emotions. You reconcile your inner differences. You no longer criticize and dismantle your character in your mind And number nine. You welcome help and support The independent survivor. Has a don’t ask for help mentality, maybe because they never got it when they needed it or because of the harsh rejection when they spoke up, They shut down to get by and decided to do it by themselves because they had no choice With healing You start to realize that as strong as you are, you can’t carry and do everything by yourself. You do need help and we all do and it’s available out there for you. You are more open to support and less afraid of having this need for assistance met. The pride and shame you might feel for asking for help are gone, because you know that it’s, okay, to let go of the heavy burden on your shoulders and have someone to lean on. Did you relate to any of these points? Do you feel that you are beginning to heal As rewarding as the first step of healing? You will run into the discomfort of your healing and this will try to make you stop to lessen or ignore the pain, but whatever you resist you prolong. If you are in the healing process, well done, I’m proud of you for doing this work and I hope you can find peace through it And if you’re not that’s, okay, because healing is a long process that takes time you’re still living and doing what you can Applaud yourselves. Did you find this video valuable, Tell us in the comments below Please like and share it with friends that might find use in this video too, and make sure to subscribe to Psych2Go and hit the notification bell for more content. All the references used are added in the description box below. Thank you for watching and see you next time…As found on YouTubeSeanCooper🗯 The Shyness & Social Guy ⇝ The 3 WORST Mistakes You Must AVOID If You Want To Overcome Shyness (PLUS: 1 weird trick that targets the root biological cause of shyness so you can stop being nervous, awkward, and quiet around people…) By Sean Cooper, The Shyness & Social Anxiety Guy. The fact that you’re reading this article tells me you may have already reached a point where you feel your shyness is NOT going away on its own… or you fear it’s getting worse and worse. And I don’t want you to waste one more day living a life where you feel left out, bored, or depressed because you don’t have the relationships which would make you happy. That’s why I’ve put together this page to help you avoid the worst mistakes that keep many people stuck with shyness for years… http://flywait.darekw.hop.clickbank.net/ often giving up hope of ever improving as you watch other people have interesting “normal” lives without you. Yet this doesn’t have to happen.
However, if you decide to it has far-reaching benefits beyond the acceptance and acknowledgment of the traumatic experience Once you are in the healing process, you are developing bravery around your emotions and your mind With this newfound conscious control. You are no longer scared by things that scared you before Scared of making a living situation change. You now are redecorating your bedroom and experimenting with paint colors. You never thought you would Go to a party you don’t know Before you would’ve recoiled at the thought, but now it’s a little less anxiety-inducing and you have a bit more confidence Number seven. You easily accept disappointments and take them in stride. Life is a balance of success and failure, light and dark ups and downs. When you’re not healing disappointments hit, you like a freight truck to the chest, knocking all of the motivation and passion out of you With healing you understand that bad days do happen and can’t be avoided, but are also temporary Any disappointments or unmet Expectations are accepted and taken in stride. You respond in better healthier ways that are less reactive Number. Eight you have more inner peace Healing brings about self-integration. If you’re a Harry Potter, fan it’s as if Voldemort brought back all of his Horcruxes and decided on becoming a better complete person who accepts the natural way of life on a soul level. And if you’re, not a fan. It’s like taking inventory of all of your experiences painful or not, and seeing yourself as the whole person You develop this inner peace because you deeply forgive yourself and you can readily forgive others too. By having this peace and integration, you are less likely to self-sabotage because you’re no longer a warring country within yourself with conflicting desires and emotions. You reconcile your inner differences. You no longer criticize and dismantle your character in your mind And number nine. You welcome help and support The independent survivor. Has a don’t ask for help mentality, maybe because they never got it when they needed it or because of the harsh rejection when they spoke up, They shut down to get by and decided to do it by themselves because they had no choice With healing You start to realize that as strong as you are, you can’t carry and do everything by yourself. You do need help and we all do and it’s available out there for you. You are more open to support and less afraid of having this need for assistance met. The pride and shame you might feel for asking for help are gone, because you know that it’s, okay, to let go of the heavy burden on your shoulders and have someone to lean on. Did you relate to any of these points? Do you feel that you are beginning to heal As rewarding as the first step of healing? You will run into the discomfort of your healing and this will try to make you stop to lessen or ignore the pain, but whatever you resist you prolong. If you are in the healing process, well done, I’m proud of you for doing this work and I hope you can find peace through it And if you’re not that’s, okay, because healing is a long process that takes time you’re still living and doing what you can Applaud yourselves. Did you find this video valuable, Tell us in the comments below Please like and share it with friends that might find use in this video too, and make sure to subscribe to Psych2Go and hit the notification bell for more content. All the references used are added in the description box below. Thank you for watching and see you next time…As found on YouTubeSeanCooper🗯 The Shyness & Social Guy ⇝ The 3 WORST Mistakes You Must AVOID If You Want To Overcome Shyness (PLUS: 1 weird trick that targets the root biological cause of shyness so you can stop being nervous, awkward, and quiet around people…) By Sean Cooper, The Shyness & Social Anxiety Guy. The fact that you’re reading this article tells me you may have already reached a point where you feel your shyness is NOT going away on its own… or you fear it’s getting worse and worse. And I don’t want you to waste one more day living a life where you feel left out, bored, or depressed because you don’t have the relationships which would make you happy. That’s why I’ve put together this page to help you avoid the worst mistakes that keep many people stuck with shyness for years… http://flywait.darekw.hop.clickbank.net/ often giving up hope of ever improving as you watch other people have interesting “normal” lives without you. Yet this doesn’t have to happen.
12 Things High Functioning Anxiety Makes you Do
Do you think you might have anxiety or know someone who does if not What’s the first image you have and you imagine someone with diagnosed anxiety? The popular comical image may have popped into your head with the frazzled jittery expression unkempt hair and profuse sweating the truth is some people go on to be successful and accomplish great things despite their battle against this mental illness This is known as high functioning anxiety isn’t a diagnosable condition And so it can be difficult to identify because those who have it don’t appear anxious However, the calm appearance doesn’t make it any less real serious or painful for those who have it Wondering now if you might fit in with this category Here are 12 things. You may not realize you’re doing this because of your high functioning anxiety 1 you turn down things you want to go to You eagerly await events and get-togethers with friends, but when the day finally comes you often decide not to go at the very last minute sound familiar Even though you were looking forward to it for so long You’ve talked yourself out of attending because the thought of going out leaves you wracked with worry and dread – you dislike having to meet new people When someone says to you, there’ll be so many new people you can network with. How do you feel? Mingling and social functions just aren’t your thing not due to shyness or introversion. You just don’t want to meet new people Sticking to your close-knit group of friends is comfortable and happy for you Introducing yourself or being introduced to someone else makes you feel self-conscious and worried about making a good first impression This worry is so intense that it sucks any enjoyment or intrigue out of meeting Someone new 3 you’re uncomfortable with slow responses The moment you send someone a text or leave them a voice message Do you start counting the seconds waiting for a response and the longer you wait? The more you feel anxious you overthink about why they haven’t replied yet and somehow take it to mean that you did something wrong Take a breath they probably like you just fine and their phone might be on mute For you get very little sleep We hear eight hours of sleep is required Can you remember the last time you got eight hours of sleep? We mean all at once not spread out over a few days You may be able to look at anxiety as the reason it may wake you up early and keep you from having a deep and relaxed sleep and also keep you up at night with thoughts racing through your mind Being shortchanged on both ends is why sleep deprivation is such a common complaint amongst those of us who suffer from high functioning anxiety Five you fixate on the tiniest details Is there any little thing you think about what’s keeping you up at night and depriving you of sleep Like how you said you to to the waiter when they told you to enjoy your meal? Or maybe why that person replied to your long text simply, okay? Logically, you realize this isn’t going to hugely impact your life. The waiter won’t remember you and that other person was probably just busy Still you examine it this fixation is a common feature for people with high-functioning Anxiety you tend to obsess over trivial things Especially social interactions you analyze everything and spend hours and hours wondering what it could all mean and why? Six you get hung up on old conversations Speaking of social interactions. Do you find yourself playing back old social scenarios in your head thinking about different actions? You could have taken or Not Taken Things like maybe I shouldn’t have texted him or maybe I should have given that witty reply High-functioning anxiety makes you overthink every single social interaction You’ve ever had big or small and it’s not unusual for people who struggle with it to get hung up on the past regardless of how long ago it was 7 your unforgiving to yourself Do you feel upset at yourself when you make a mistake? Mulling over it and scolding yourself for months even years Well high functioning anxiety can often resemble perfectionism With one of its most problematic characteristics being that it turns us against ourselves whenever we mess up Your anxiety makes that mistake bigger in your point of view than it was in reality.  So getting over it feels difficult Eight you constantly compare yourself to others It’s normal to occasionally compare yourself to others but those with high-functioning anxiety. Take it to an extreme Are you overly concerned with how you measure up against your peers? Do you constantly worry that you’re not fulfilling your full potential? No matter how much you accomplish. Do you never feel like it’s enough? If so, you might be struggling with high-functioning anxiety 9 You’re a constant people pleaser Do you work hard to make others feel happy, even if it comes at the cost of your well-being Do you feel like you’ll never be good enough until you attain it? Everyone’s approval If you have high-functioning anxiety you may have convinced yourself that the only way others will ever accept you is if you go above and beyond what everyone expects of You all the time. 10 You need to keep yourself busy all the time Now we’re not talking about creating great Renaissance artworks or intricate business plans We just mean busy not necessarily productive If you’re not busy you feel Restless and tense. So you try to occupy yourself with just about anything during your nails. Yes Alphabetizing your games. Okay, cleaning your perfectly working computer fan with a toothbrush It’s sure the truth is you don’t mind doing anything as long as it helps distract yourself from your thoughts and worries 11 You get very anxious whenever you think about the future What does the future mean to you for many in the future is the light of possibility something to eagerly look forward to? then for some, it can feel like Scrooge and that last spirit of Christmas who looked like the Grim Reaper if You’re not feeling hope but terror and dread for what’s to come This could be a sign of high-functioning anxiety can paralyze you with fear about the unknown and what’s not in your control it can keep you from truly living your life to the fullest because you always expect the worst to happen and 12 you always focus on the worst-case scenario Do you like to prep my prep? We mean do you say to yourself? Okay, so this is the worst possible outcome I’ll be ready for it. If I’m ready for it. I can handle anything else. Do you then continue to expect the worst-case scenario? They might be high-functioning anxiety laying the plans This might lead people to misjudge you as a pessimist because ultimately you may try to share with them your preparations Where you see anticipating and being proactive they see a downer Unfortunately being so prepared often doesn’t allow you to just enjoy the moment Do you relate to any of the things listed here living with high-functioning anxiety is never easy? But most people may not see the emotional toll it can have on a person if you’re starting to feel overwhelmed with your anxiety There are many professional certified resources to reach out to Please like share and subscribe to the site to go for more psychology content.
So getting over it feels difficult Eight you constantly compare yourself to others It’s normal to occasionally compare yourself to others but those with high-functioning anxiety. Take it to an extreme Are you overly concerned with how you measure up against your peers? Do you constantly worry that you’re not fulfilling your full potential? No matter how much you accomplish. Do you never feel like it’s enough? If so, you might be struggling with high-functioning anxiety 9 You’re a constant people pleaser Do you work hard to make others feel happy, even if it comes at the cost of your well-being Do you feel like you’ll never be good enough until you attain it? Everyone’s approval If you have high-functioning anxiety you may have convinced yourself that the only way others will ever accept you is if you go above and beyond what everyone expects of You all the time. 10 You need to keep yourself busy all the time Now we’re not talking about creating great Renaissance artworks or intricate business plans We just mean busy not necessarily productive If you’re not busy you feel Restless and tense. So you try to occupy yourself with just about anything during your nails. Yes Alphabetizing your games. Okay, cleaning your perfectly working computer fan with a toothbrush It’s sure the truth is you don’t mind doing anything as long as it helps distract yourself from your thoughts and worries 11 You get very anxious whenever you think about the future What does the future mean to you for many in the future is the light of possibility something to eagerly look forward to? then for some, it can feel like Scrooge and that last spirit of Christmas who looked like the Grim Reaper if You’re not feeling hope but terror and dread for what’s to come This could be a sign of high-functioning anxiety can paralyze you with fear about the unknown and what’s not in your control it can keep you from truly living your life to the fullest because you always expect the worst to happen and 12 you always focus on the worst-case scenario Do you like to prep my prep? We mean do you say to yourself? Okay, so this is the worst possible outcome I’ll be ready for it. If I’m ready for it. I can handle anything else. Do you then continue to expect the worst-case scenario? They might be high-functioning anxiety laying the plans This might lead people to misjudge you as a pessimist because ultimately you may try to share with them your preparations Where you see anticipating and being proactive they see a downer Unfortunately being so prepared often doesn’t allow you to just enjoy the moment Do you relate to any of the things listed here living with high-functioning anxiety is never easy? But most people may not see the emotional toll it can have on a person if you’re starting to feel overwhelmed with your anxiety There are many professional certified resources to reach out to Please like share and subscribe to the site to go for more psychology content. We hope to see you in the next video and as always Thanks so much for watching.As found on YouTubeSeanCooper🗯 The Shyness & Social Guy ⇝ The 3 WORST Mistakes You Must AVOID If You Want To Overcome Shyness (PLUS: 1 weird trick that targets the root biological cause of shyness so you can stop being nervous, awkward, and quiet around people…) By Sean Cooper, The Shyness & Social Anxiety Guy. The fact that you’re reading this article tells me you may have already reached a point where you feel your shyness is NOT going away on its own… or you fear it’s getting worse and worse. And I don’t want you to waste one more day living a life where you feel left out, bored, or depressed because you don’t have the relationships which would make you happy. That’s why I’ve put together this page to help you avoid the worst mistakes that keep many people stuck with shyness for years… http://flywait.darekw.hop.clickbank.net/ often giving up hope of ever improving as you watch other people have interesting “normal” lives without you. Yet this doesn’t have to happen.
We hope to see you in the next video and as always Thanks so much for watching.As found on YouTubeSeanCooper🗯 The Shyness & Social Guy ⇝ The 3 WORST Mistakes You Must AVOID If You Want To Overcome Shyness (PLUS: 1 weird trick that targets the root biological cause of shyness so you can stop being nervous, awkward, and quiet around people…) By Sean Cooper, The Shyness & Social Anxiety Guy. The fact that you’re reading this article tells me you may have already reached a point where you feel your shyness is NOT going away on its own… or you fear it’s getting worse and worse. And I don’t want you to waste one more day living a life where you feel left out, bored, or depressed because you don’t have the relationships which would make you happy. That’s why I’ve put together this page to help you avoid the worst mistakes that keep many people stuck with shyness for years… http://flywait.darekw.hop.clickbank.net/ often giving up hope of ever improving as you watch other people have interesting “normal” lives without you. Yet this doesn’t have to happen.
 So getting over it feels difficult Eight you constantly compare yourself to others It’s normal to occasionally compare yourself to others but those with high-functioning anxiety. Take it to an extreme Are you overly concerned with how you measure up against your peers? Do you constantly worry that you’re not fulfilling your full potential? No matter how much you accomplish. Do you never feel like it’s enough? If so, you might be struggling with high-functioning anxiety 9 You’re a constant people pleaser Do you work hard to make others feel happy, even if it comes at the cost of your well-being Do you feel like you’ll never be good enough until you attain it? Everyone’s approval If you have high-functioning anxiety you may have convinced yourself that the only way others will ever accept you is if you go above and beyond what everyone expects of You all the time. 10 You need to keep yourself busy all the time Now we’re not talking about creating great Renaissance artworks or intricate business plans We just mean busy not necessarily productive If you’re not busy you feel Restless and tense. So you try to occupy yourself with just about anything during your nails. Yes Alphabetizing your games. Okay, cleaning your perfectly working computer fan with a toothbrush It’s sure the truth is you don’t mind doing anything as long as it helps distract yourself from your thoughts and worries 11 You get very anxious whenever you think about the future What does the future mean to you for many in the future is the light of possibility something to eagerly look forward to? then for some, it can feel like Scrooge and that last spirit of Christmas who looked like the Grim Reaper if You’re not feeling hope but terror and dread for what’s to come This could be a sign of high-functioning anxiety can paralyze you with fear about the unknown and what’s not in your control it can keep you from truly living your life to the fullest because you always expect the worst to happen and 12 you always focus on the worst-case scenario Do you like to prep my prep? We mean do you say to yourself? Okay, so this is the worst possible outcome I’ll be ready for it. If I’m ready for it. I can handle anything else. Do you then continue to expect the worst-case scenario? They might be high-functioning anxiety laying the plans This might lead people to misjudge you as a pessimist because ultimately you may try to share with them your preparations Where you see anticipating and being proactive they see a downer Unfortunately being so prepared often doesn’t allow you to just enjoy the moment Do you relate to any of the things listed here living with high-functioning anxiety is never easy? But most people may not see the emotional toll it can have on a person if you’re starting to feel overwhelmed with your anxiety There are many professional certified resources to reach out to Please like share and subscribe to the site to go for more psychology content.
So getting over it feels difficult Eight you constantly compare yourself to others It’s normal to occasionally compare yourself to others but those with high-functioning anxiety. Take it to an extreme Are you overly concerned with how you measure up against your peers? Do you constantly worry that you’re not fulfilling your full potential? No matter how much you accomplish. Do you never feel like it’s enough? If so, you might be struggling with high-functioning anxiety 9 You’re a constant people pleaser Do you work hard to make others feel happy, even if it comes at the cost of your well-being Do you feel like you’ll never be good enough until you attain it? Everyone’s approval If you have high-functioning anxiety you may have convinced yourself that the only way others will ever accept you is if you go above and beyond what everyone expects of You all the time. 10 You need to keep yourself busy all the time Now we’re not talking about creating great Renaissance artworks or intricate business plans We just mean busy not necessarily productive If you’re not busy you feel Restless and tense. So you try to occupy yourself with just about anything during your nails. Yes Alphabetizing your games. Okay, cleaning your perfectly working computer fan with a toothbrush It’s sure the truth is you don’t mind doing anything as long as it helps distract yourself from your thoughts and worries 11 You get very anxious whenever you think about the future What does the future mean to you for many in the future is the light of possibility something to eagerly look forward to? then for some, it can feel like Scrooge and that last spirit of Christmas who looked like the Grim Reaper if You’re not feeling hope but terror and dread for what’s to come This could be a sign of high-functioning anxiety can paralyze you with fear about the unknown and what’s not in your control it can keep you from truly living your life to the fullest because you always expect the worst to happen and 12 you always focus on the worst-case scenario Do you like to prep my prep? We mean do you say to yourself? Okay, so this is the worst possible outcome I’ll be ready for it. If I’m ready for it. I can handle anything else. Do you then continue to expect the worst-case scenario? They might be high-functioning anxiety laying the plans This might lead people to misjudge you as a pessimist because ultimately you may try to share with them your preparations Where you see anticipating and being proactive they see a downer Unfortunately being so prepared often doesn’t allow you to just enjoy the moment Do you relate to any of the things listed here living with high-functioning anxiety is never easy? But most people may not see the emotional toll it can have on a person if you’re starting to feel overwhelmed with your anxiety There are many professional certified resources to reach out to Please like share and subscribe to the site to go for more psychology content. We hope to see you in the next video and as always Thanks so much for watching.As found on YouTubeSeanCooper🗯 The Shyness & Social Guy ⇝ The 3 WORST Mistakes You Must AVOID If You Want To Overcome Shyness (PLUS: 1 weird trick that targets the root biological cause of shyness so you can stop being nervous, awkward, and quiet around people…) By Sean Cooper, The Shyness & Social Anxiety Guy. The fact that you’re reading this article tells me you may have already reached a point where you feel your shyness is NOT going away on its own… or you fear it’s getting worse and worse. And I don’t want you to waste one more day living a life where you feel left out, bored, or depressed because you don’t have the relationships which would make you happy. That’s why I’ve put together this page to help you avoid the worst mistakes that keep many people stuck with shyness for years… http://flywait.darekw.hop.clickbank.net/ often giving up hope of ever improving as you watch other people have interesting “normal” lives without you. Yet this doesn’t have to happen.
We hope to see you in the next video and as always Thanks so much for watching.As found on YouTubeSeanCooper🗯 The Shyness & Social Guy ⇝ The 3 WORST Mistakes You Must AVOID If You Want To Overcome Shyness (PLUS: 1 weird trick that targets the root biological cause of shyness so you can stop being nervous, awkward, and quiet around people…) By Sean Cooper, The Shyness & Social Anxiety Guy. The fact that you’re reading this article tells me you may have already reached a point where you feel your shyness is NOT going away on its own… or you fear it’s getting worse and worse. And I don’t want you to waste one more day living a life where you feel left out, bored, or depressed because you don’t have the relationships which would make you happy. That’s why I’ve put together this page to help you avoid the worst mistakes that keep many people stuck with shyness for years… http://flywait.darekw.hop.clickbank.net/ often giving up hope of ever improving as you watch other people have interesting “normal” lives without you. Yet this doesn’t have to happen.5 Differences Between Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Anxiety
[Music] hi everyone we it’s like to go would love to thank you for making us a digital family of more than 2 million it’s with your continued support that we’re able to bring you new content regularly our mission is to help everyone become more self aware of the various psychological factors that affect our lives one such factor that we hear about on a daily basis is anxiety but it’s important to know when it’s anxiety only and wanted to become something more so let’s find out anxiety in general is our normal reaction to stress in fact it can be a good thing anxiety motivates you to accomplish your assignments to study harder for a test and it can warn you when you’re in a dangerous situation it informs you to be extra vigilant about your environment the fight or flee generalized anxiety disorder or GED on the other hand is a full-fledged anxiety disorder that involves intense and excessive anxiety as a key factor along with other debilitating symptoms differentiating between normal anxiety and generalized anxiety disorder or di D can be tricky how do you know especially if you’re a little more anxious than others whether or not your anxiety is significant enough to qualify as a disorder so let’s begin with an introduction to the main concepts revolving around the – one normal anxiety is more of a friend than a foe according to the anxiety and depression Association of America anxiety is a normal and often healthy emotion which is characterized by feelings of tension worried thoughts and physical changes like increased blood pressure when we face potentially harmful or worrying triggers feelings of anxiety are not only normal but necessary for survival since the earliest days the approach of predators an incoming danger set off alarms in the body and allowed evasive action these alarms were in the form of a raised heartbeat sledding and increased sensitivity to surroundings danger causes a rush of adrenaline a hormone in the brain which in turn triggers the anxious reactions in a process called the fight-or-flight response this prepares humans to physically confront or flee any potential threats to sea all these are classic characteristics of normal anxiety such traits came in handy for our predecessors but we don’t have to be in a constant state of fight-or-flight anymore so running from larger animals is a less pressing concern in present times than it would have been for early humans anxieties now revolve around work money family life health and other crucial issues that demand a person’s attention without necessarily requiring the fight-or-flight reaction the nervous feeling before an important life event are during a difficult situation is a natural echo of the original fight-or-flight reaction it can still be essential to survival anxiety about being hit by a car when crossing the street for example means that a person will instinctively look both ways to avoid danger when the duration or severity of an anxious feeling is out of proportion to the original trigger or stressor physical symptoms such as increased blood pressure and nausea may also develop these responses are what moved normal anxiety beyond into gid generalized anxiety disorder GA D is when the trouble starts generalized anxiety disorder involves persistent and excessive worry that interferes with daily activities people with symptoms of GA D tend to always expect disaster and can stop worrying about health money family work or school in people with GID the worry is often unrealistic or out of proportion from the situation daily life becomes a constant state of worry fear and dread eventually the anxiety so dominates the person’s thinking that it interferes with daily functioning including work school social activities and relationships there are several key differences that make them distinguishable here are a few ways you can tell the two apart one presence of a stressor usually a normal anxiety occurs in response to a stressor such as an exam an upcoming interview a fight with a friend or a new job when you struggle with GID you’re anxious most or almost all of the time even when you can’t spot the source of the stress for instance people a generalized anxiety disorder can have a difficult time just getting through the day even seemingly small responsibilities like paying the bills make them feel anxious – intensity and length gid produces intense and excessive emotional responses even if you’re reacting to a stressor your anxiety is disproportionate to that stressor many people are on the edge before an exam but a person with jad might be anxious several weeks beforehand and will experience intense symptoms right before and during the exam also normal anxiety is fleeting while gid is ongoing and the feelings can last weeks or months three physical symptoms of jad excessive anxiety and wary aren’t the only symptoms that accompany GID there are physical symptoms – dizziness lightheadedness sweating trembling heart pounding headaches and nausea you feel like you can’t breathe can’t talk or have to go to the bathroom frequently people at jad also report feeling detachment and disconnected from reality they feel like they can’t think straight and have difficulty concentrating psychological symptoms are also present individuals experience racing or negative thoughts and are unable to concentrate and have worries about day to day things or impairment when you struggle with GID it affects your entire life it impairs or interferes with your schoolwork job and daily life avoidance is a symptom of jad and can be quite debilitating in other words excessive anxiety can cause you to avoid normal activities you might skip class miss a test stop going to work procrastinate grocery shopping or avoid anything that makes you feel anxious and 5 no control most people can reduce and control their anxiety through a variety of coping techniques and the ability to calm oneself however people at GID have significant difficulty finding relaxation calm and time away from their worries if you have more difficulty than other people you know in controlling your anxiety it may be more than normal anxiety did you often find yourself confused about these two conditions do these factors easier to differentiate between the two do let us know in the comments below if you are struggling with overwhelming anxiety and you can relate to some of these factors don’t hesitate to seek help from a mental health professional and subsequent treatment also remember to share this video with someone you think might benefit from these as well don’t forget to click the like button and subscribe for more content as always thanks for watching  As found on YouTubeSeanCooper🗯 The Shyness & Social Guy ⇝ The 3 WORST Mistakes You Must AVOID If You Want To Overcome Shyness (PLUS: 1 weird trick that targets the root biological cause of shyness so you can stop being nervous, awkward, and quiet around people…) By Sean Cooper, The Shyness & Social Anxiety Guy. The fact that you’re reading this article tells me you may have already reached a point where you feel your shyness is NOT going away on its own… or you fear it’s getting worse and worse. And I don’t want you to waste one more day living a life where you feel left out, bored, or depressed because you don’t have the relationships which would make you happy. That’s why I’ve put together this page to help you avoid the worst mistakes that keep many people stuck with shyness for years… often giving up hope of ever improving as you watch other people have interesting “normal” lives without you. Yet this doesn’t have to happen.
As found on YouTubeSeanCooper🗯 The Shyness & Social Guy ⇝ The 3 WORST Mistakes You Must AVOID If You Want To Overcome Shyness (PLUS: 1 weird trick that targets the root biological cause of shyness so you can stop being nervous, awkward, and quiet around people…) By Sean Cooper, The Shyness & Social Anxiety Guy. The fact that you’re reading this article tells me you may have already reached a point where you feel your shyness is NOT going away on its own… or you fear it’s getting worse and worse. And I don’t want you to waste one more day living a life where you feel left out, bored, or depressed because you don’t have the relationships which would make you happy. That’s why I’ve put together this page to help you avoid the worst mistakes that keep many people stuck with shyness for years… often giving up hope of ever improving as you watch other people have interesting “normal” lives without you. Yet this doesn’t have to happen. 
 As found on YouTubeSeanCooper🗯 The Shyness & Social Guy ⇝ The 3 WORST Mistakes You Must AVOID If You Want To Overcome Shyness (PLUS: 1 weird trick that targets the root biological cause of shyness so you can stop being nervous, awkward, and quiet around people…) By Sean Cooper, The Shyness & Social Anxiety Guy. The fact that you’re reading this article tells me you may have already reached a point where you feel your shyness is NOT going away on its own… or you fear it’s getting worse and worse. And I don’t want you to waste one more day living a life where you feel left out, bored, or depressed because you don’t have the relationships which would make you happy. That’s why I’ve put together this page to help you avoid the worst mistakes that keep many people stuck with shyness for years… often giving up hope of ever improving as you watch other people have interesting “normal” lives without you. Yet this doesn’t have to happen.
As found on YouTubeSeanCooper🗯 The Shyness & Social Guy ⇝ The 3 WORST Mistakes You Must AVOID If You Want To Overcome Shyness (PLUS: 1 weird trick that targets the root biological cause of shyness so you can stop being nervous, awkward, and quiet around people…) By Sean Cooper, The Shyness & Social Anxiety Guy. The fact that you’re reading this article tells me you may have already reached a point where you feel your shyness is NOT going away on its own… or you fear it’s getting worse and worse. And I don’t want you to waste one more day living a life where you feel left out, bored, or depressed because you don’t have the relationships which would make you happy. That’s why I’ve put together this page to help you avoid the worst mistakes that keep many people stuck with shyness for years… often giving up hope of ever improving as you watch other people have interesting “normal” lives without you. Yet this doesn’t have to happen.