https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0nz0iaNvVpE
[Music] depending on your perspective Emanuel Kant was either the most boring person on the planet or a productivity Hacker’s wet dream for over 40 years he woke up every morning at 5:00 a.m. and wrote for exactly 3 hours he would then lecture at the same University for exactly 4 hours he
00:00:27followed that up with lunch at the same restaurant each day then in the afternoon he would go on an extended walk through the same park on the same route leaving and returning home at the exact same time every day K spent his entire life in kbur Prussia I mean that literally he never left the
00:00:46city despite the ca being an hour away he never saw it Kant was efficiency personified he was so mechanical on his habits that his neighbors joke that they could tune their clocks based on when he left his apartment each day he would would leave for his daily walk at 3:30 p.m. have dinner with
00:01:03the same friend every evening and return home to finish work and go to bed at exactly 10 p.m. it’s easy for us to scoff at a guy like this what a loser seriously get a life dude but K was one of the most important and influential thinkers in modern history he did more to steer the world
00:01:20from his single room apartment in Prussia than most Kings and armies ever did before or since if you’re living in a Democratic Society that protects indiv idual rights you have can’t to partially thank for that he was the first person to ever Envision a global governing body that
00:01:37would guarantee peace across much of the world he prescribed SpaceTime in such a way that it later inspired Einstein’s discovery of Relativity he came up with the idea that animals could potentially have rights themselves he invented the philosophy of Aesthetics and beauty and resolved
00:01:51a 200-year philosophical debate in the span of a couple hundred Pages he reinvented moral Philosophy from top to bottom over throwing ideas that had been the basis of Western Civilization since Aristotle Kant was an intellectual badass if brains had balls K would have been made out
00:02:09of steel his ideas particularly about ethics are still discussed and debated in thousands of universities today and that’s what I want to talk about K’s moral philosophy and why it matters now you might be saying really moral philosophy who cares man show me a shiny Sunset inspirational
00:02:29quote or a cat meme well that right there is moral philosophy anytime you say who cares or what’s the big deal you’re essentially questioning the value of something is it worth your time and attention is it better or worse than something else these are all questions of value and they
00:02:48all fall under the umbrella of moral philosophy our moral philosophy determines what we value what we care about and what we don’t care about and our values determine our decisions actions and beliefs therefore moral philosophy applies to everything in our lives got it kant’s moral philosophy is
00:03:07unique and counterintuitive can’t believe that for something to be good it had to be Universal that is it can’t be right to do something in one situation and wrong to do it in another if lying is wrong it has to be wrong all the time it has to be wrong when everyone does it period if it isn’t
00:03:25always right or always wrong then it cannot be a valid ethical principle Kant these universalized ethical principles categorical imperatives rules to live by that are valid in all contexts in every situation to every human being well holy [ __ ] universal laws that dictate all morality for every
00:03:44human being sure you want fries with that it’s so impossible it sounds ludicrous but Kant made a hell of an attempt in fact he made a number of attempts at creating categorical imperatives some of those attempts were quickly ripped the shreds by other philosophers but others have actually
00:04:00held up the test of time to some degree one of them in particular has kind of stuck and in all of my years reading and studying philosophy psychology and other Sciences it is one of the most powerful statements that I’ve ever come across its implications reach into every part of
00:04:16each person’s life in a single sentence it sums up the bulk of all of our ethical intuitions and assumptions and in each situation it points to a clear direction of how we should be acting and why okay enough foreplay here’s kant’s rule act that you use Humanity whether in your own person or in
00:04:36a person of any other always at the same time as an end and never merely as a means okay what the actual [ __ ] let’s back up for a second can’t believe that rationality was sacred when I say rationality I don’t mean like Sudoku or chess Grandmaster rationality I mean rationality as
00:04:56the fact that we are the only known creatures in the universe that are able to make the decisions weigh options and consider the moral implications of each and every action basically Consciousness to the only thing that distinguishes us from the rest of the universe is our ability to process
00:05:10information and act consciously in the world and this to him is special it’s exceedingly special for all we know we are the only shot the universe has at intelligent self organization therefore we need to take it seriously and therefore rationality and protecting conscious Choice
00:05:28must be the basis for all of our moral reasoning Kant wrote that quote without rationality the universe would be a waste in vain and without purpose to K’s mind without intelligence and the freedom to exercise that intelligence we might as well just be a bunch of rocks nothing would
00:05:45matter therefore Kant believed that all morality is derived from the protection and promotion of rational Consciousness in each individual so how do you do that well cons rule above let’s restate State con rule in a more modern language to make it more easily digestible quote each person must
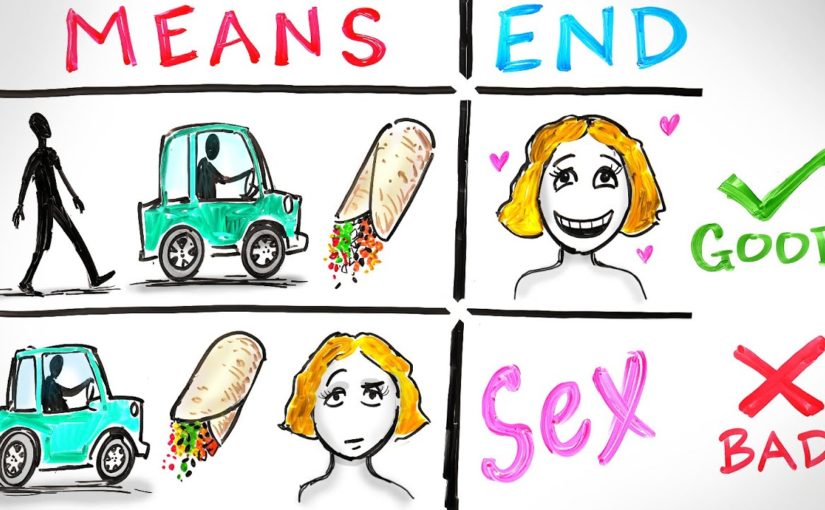
00:06:05never be treated only as a means to some other end but also be treated as an end themselves okay let’s say I’m hungry and I want a burrito I get in the car and I drive to Chipotle and I order my usual double meat monster that makes me oh so happy on a weekly basis in this situation eating
00:06:23the burrito is my end goal it’s ultimately why I’m doing everything else getting in the car driving buying gas and so on all these things I do to get the burrito are the means I.E the things that I must do in order to achieve my end if you call a friend to find out how they’re doing calling them
00:06:41is a means finding out how they’re doing is your end if you leave a party early so you can wake up in the morning leaving the party is the means and waking up early is your end means are things that we do conditionally I don’t want to get in my car and drive but I want a burrito therefore
00:06:58driving is the means to my burrito end an end is something that is desired for its own sake it is the defining motivating factor of our decisions and behaviors if I wanted to eat a burrito only because my wife wanted a burrito and I wanted to make her happy then the burrito is no longer
00:07:15my end it is now a means to an even greater end making my wife happy and if I only wanted to make my wife happy so I could hopefully get laid tonight now my wife’s happiness is a means to a greater end of sex likely that last example made you squirm a little bit and think I’m kind
00:07:31of a dirt bag and that’s exactly what Kant is talking about his argument hell his rule states that treating any human being as a means to some other end is the basis of all unethical Behavior so treating a burrito as a means to my wife’s end is fine after all as far as I know burritos
00:07:49don’t have rational Consciousness but if I treat my wife as a means to the end of sex now I am treating her as a means and Kant would argue that that is some shade of wrong let’s give K’s Rule The Common Sense check lying is wrong because you are misleading another person’s conscious
00:08:05behavior in order to achieve your own goal you are therefore treating that person as a means to your own end therefore lying is unethical cheating is unethical for a similar reason you are violating the expectations of other rational and sentient beings for your own personal aims
00:08:21you are treating the rules and expectations agreed to with others as a means to your own personal end that is wrong violence same deal you were treating another person as a means to some greater political or personal end bad very bad cons formulation checks all the boxes that
00:08:38we would expect from a theory of morality but it goes Way Way Beyond Common Sense Morality In fact I will try to argue that K rule plausibly extends to pretty much everything that we value is right and good today check it out the moral implications of K’s rule the list below is incomplete some of
00:08:56the items K explicitly wrote about but others are extrapolations that I’ve taken from his work and applied to my own values my hope is that by the end of it you will see the incredible flexibility of the single moral maximum to extend almost all areas of human life example one laziness okay I
00:09:14can be as lazy is the next Guy full disclosure and I often feel guilty about it but we all know that [ __ ] off in the short term inevitably harms Us in the long term but for whatever reason this short-term gain versus long-term loss calculation never seems to inspire or move us but that’s not
00:09:30why Kant thinks it’s wrong in fact Kant would say that this is the wrong way to think about laziness it’s insufficient comp believed that we all had a moral imperative to do the best that we can at all times but he didn’t say to do your best because of self-esteem or personal utility or contributing to
00:09:47society or whatever he went even further than that he argued you should do your best because anything less is to treat ourselves as a means rather than an end yes you can treat yourself as a means as well you’re sitting on the couch refreshing Twitter for the 28th time and you’re
00:10:03treating your mind and your attention as a mere pleasure receptacle you are not maximizing the potential of your Consciousness in fact you are using your Consciousness as a means to stimulate your emotional ends this is not only bad Kant would argue but it’s unethical you are actively
00:10:19harming yourself example two addiction Believe It or Not Kant wasn’t a total party pooper he enjoyed some wine with his lunch he smoked the pipe but only at the same time each morning and only one bowl of tobacco Kant was not necessarily anti-un what he was against though was pure escapism
00:10:38he wrote that using alcohol or other means of escaping one’s own life was unethical because it requires you to use your rational mind and freedom as a means to some other end in this case getting [ __ ] up comp believed in facing one’s problems he believed that suffering is
00:10:52sometimes warranted and even necessary in life we tend to judge the immorality of addiction by the damage it causes to others but Kant believed that first overindulgence was fundamentally the act of being immoral to oneself the harm it did to others was merely collateral damage it
00:11:09was a failure to confront the reality of one’s own mind and Consciousness and this failure is akin to lying to oneself or cheating oneself out of precious life potential and to can’t lying to yourself is just as unethical as lying to others example three people pleasing and seeking approval
00:11:27okay I know it’s not a good strategy to be kissing people’s asses all the time but unethical really isn’t being really nice to people and making them happy an ethical thing to do well not necessarily seeking approval in people pleasing forces you to alter your actions and speech to no longer
00:11:45reflect what you actually think and feel so right there you are already treating yourself as a means rather than an end but it gets worse because if you alter your speech and behavior in order to make others like you then you are also treating them as a means to your end you
00:12:01are altering and manipulating their perceptions of you in order to Garner a pleasant response from them K would undoubtedly argue that this is also unethical how dare you tell me my shirt looks good on me you ethical piece of [ __ ] I’ve written that length about how people pleasing and
00:12:16seeking approval leads to toxic relationships but again as usual Kant takes it even further because Kant was [ __ ] hardcore like that example four manipulation or coercion even if you’re not lying but you’re communicating with an attitude and a purpose of gaining something from
00:12:34someone without their full knowledge or explicit consent then you are being unethical K was big on fully informed consent he believed it was the only way for there to be healthy interactions between individuals it was Radical for his time and it’s something that people still struggle to
00:12:49accept today there are two areas in the modern world where I think that consent issue is huge and K would have a lot to say about it the first is obvious sex and dating under K’s rule anything short of explicit fully informed and fully sober consent is ethically out of bounds this is a hot
00:13:06button issue today and I personally think people make it far more complicated than it needs to be it basically just means being respectful people assume this means asking for permission 20 times on a date but it’s not all you have to do is State how you feel ask them how they feel and
00:13:21then respect whatever response comes back to you that’s it it’s not complicated respect was also sacred within K’s moral framework because Kant believe that all conscious creatures have a fundamental dignity that must be respected at all times and by everyone for Kant consent was the act
00:13:38of demonstrating respect anything that didn’t lead towards consent between two people was to some degree disrespectful I know that makes Kant sound like an angry grandmother but the implications of the consent issue are far reaching and wide touching every human relationship that we have
00:13:53the other modern area that is problematic is sales and advertising pretty much every marketing tactic is built around treating people as a means to some end that is making money in fact Kant struggled much of his life with the ethical implications of capitalism and wealth inequality he believed that
00:14:10it was impossible for anyone to amass a fortune without some degree of manipulation or coercion along the way therefore he was dubious of the entire system he wasn’t anti- capitalist per se and communism didn’t exist yet but the Staggering wealth inequality of his time did make him uneasy
00:14:27he believed Anyone Who Had Mass the fortune had a moral imperative to give much of it away to the starving masses example five bigotry might as well throw it in here especially since Enlightenment thinkers were Infamous for having pretty racist views which were common in the time
00:14:43interestingly K despite saying some pretty awful [ __ ] about race early in his career turned the intellectual corner and realized later in his life that no race has any right to subjugate any other it makes sense after all racism and other forms of bigotry are textbook cases of treating other
00:14:58people as means rather than ends Kant came to the conclusion that if all rationality is sacred then there’s nothing permitting European special privileges over any other nations or races he also became vehemently anti-colonialist K argued that regardless of race the violence
00:15:14and oppression required to subjugate populations would destroy people’s Humanity in the process it was the ultimate unethical institution this was completely radical for the time radical to the point of being considered absurd by many but Kant reasoned that the only way to prevent
00:15:29war and oppression was to form an international government that organized and bound nation states together centuries later the United Nations would largely be based on his vision example six the duty of self-improvement most philosophers of the Enlightenment believed that the best way to live
00:15:46was to increase happiness as much as possible and to reduce suffering as much as possible as well this approach to ethics is called utilitarianism and is still the predominant view held by many thinkers today K had a completely different take on how to go about improving the world let’s call
00:16:01it the Michael Jackson Maxim because K like Michael believed that if you want to make the world a better place take a look at yourself and make that change but instead of grabbing his crotch comp made his argument with brutal rationality and here’s how he argued it comp
00:16:16believed that generally it is impossible to know whether a person deserves to be happy or suffer because you can never truly know what their intentions and aims were when they acted similarly even if you should make others happy there’s no way to precisely know how to make them happy you
00:16:31do not know their feelings values or expectations you do not know the implications your actions will have on them on top of that what actually constitutes suffering or happiness in most non-extreme situations is unclear your divorce may cause you incredible pain today but in a year
00:16:47it might be the best thing that ever happened to you you may relish the joy of a celebration with friends but maybe it’s distracting you from pursuing something that would prevent more future suffering therefore K argued the the only logical way to improve the world is through improving
00:17:01ourselves this is because the only thing we can truly experience with any certainty is ourselves K defined self-improvement is developing the ability to adhere to the categorical imperative and he saw self-improvement as a duty an undebatable obligation put on us all to K the
00:17:17reward or punishment for not following one’s duty was not in heaven or hell but in a life made for oneself adherence to morality produced not only a better life for yourself but a better life for all those around you similarly failure to adhere to morality would produce unnecessary
00:17:33suffering for oneself and for those around you con rule has a ripple effect your improved ability to be honest with yourself will increase how honest you are with others and your honesty with others will influence them to be more honest with themselves which will then help them improve
00:17:48their lives this is true for all aspects of K’s rule whether it’s honesty productivity charity or consent the Michael Jackson Maxum suggest that kant’s rule once adopted by enough people will generate a snowball effect in the world enacting more positive change than any calculated policy
00:18:04or institution the duty of self-respect Kant intuitively understood that there is a fundamental link between our respect for ourselves and our respect for the world the way we interact with our own psyche is the template which we apply to our interactions with others and little progress
00:18:22can be made with others until we’ve made progress with ourselves he would likely be disgusted with the self-esteem movement today seeing it as just another way of treating people as a means to some end of feeling better self-respect isn’t about feeling better self-respect is about knowing
00:18:37your own value knowing that every human no matter who they are deserves basic rights and dignities that every Consciousness is sacred and must be treated as such Kant would argue that telling ourselves that we are worthless and shitty is just as wrong as telling others that they are
00:18:52worthless and shitty lying to ourselves is just as unethical as lying to others harming ourselves is just as repugnant as harming others self-love and self-care are therefore not something you learn about or practice they are something you are ethically called on to cultivate within yourself
00:19:08even if they are all you have left the impact of kant’s philosophy Khan’s philosophy if you dive into it is riddled with inconsistencies and issues but the power of His original ideas is undoubtedly changed the world and strangely when I came across them a year ago they changed
00:19:25me I had spent most of my 20s pursuing many of the items on the list above but I pursued them for practical and transactional reasons I pursued them as a means because I thought that they would make my life better meanwhile the more I worked at it the emptier I felt but reading Kant was an
00:19:41epiphany and only 80 Pages Kant Swept Away decades worth of assumptions and beliefs he showed me that what you actually do doesn’t matter as much as the purpose behind doing it and until you find the right purpose you haven’t found much of anything at all K wasn’t always a hum drum roue obsessed
00:19:58dork he wasn’t always the mayor of boreville in fact in kant’s younger years he was a bit of a party Hound as well he would stay up late drinking wine and playing cards with his friends he’d sleep late and eat too much and host big parties it wasn’t until he turned 40 that he dropped it
00:20:13all and developed the routine life he later made famous he said that he developed this routine at 40 because he realized the moral implications of his actions and decided that he would no longer allow himself to waste the precious time or energy his Consciousness had left Kant called this
00:20:28developing character AKA building a life designed around maximizing your own potential he believed most people can’t develop true character until they reach middle age because until then they are still too seduced by the fancies and whims of the world blown this way and that from excitement
00:20:44to Despair and back again we’re too obsessed with accumulating more means and are hopelessly oblivious to the ends that drive us to develop character a person must Master their own actions and master themselves and while few of us can accomplish that in a lifetime Kant believed
00:21:00it’s something we each have a duty to work towards in fact he believed it was the only thing to work [Music] towards what’s up everybody Mark Manson here and what you just heard is an excerpt from the number one New York Times bestseller everything is [ __ ] a book about
00:21:23Hope be sure to check it out and uh check out my YouTube channel it’s um you’re on [Music] [Music] YouTube